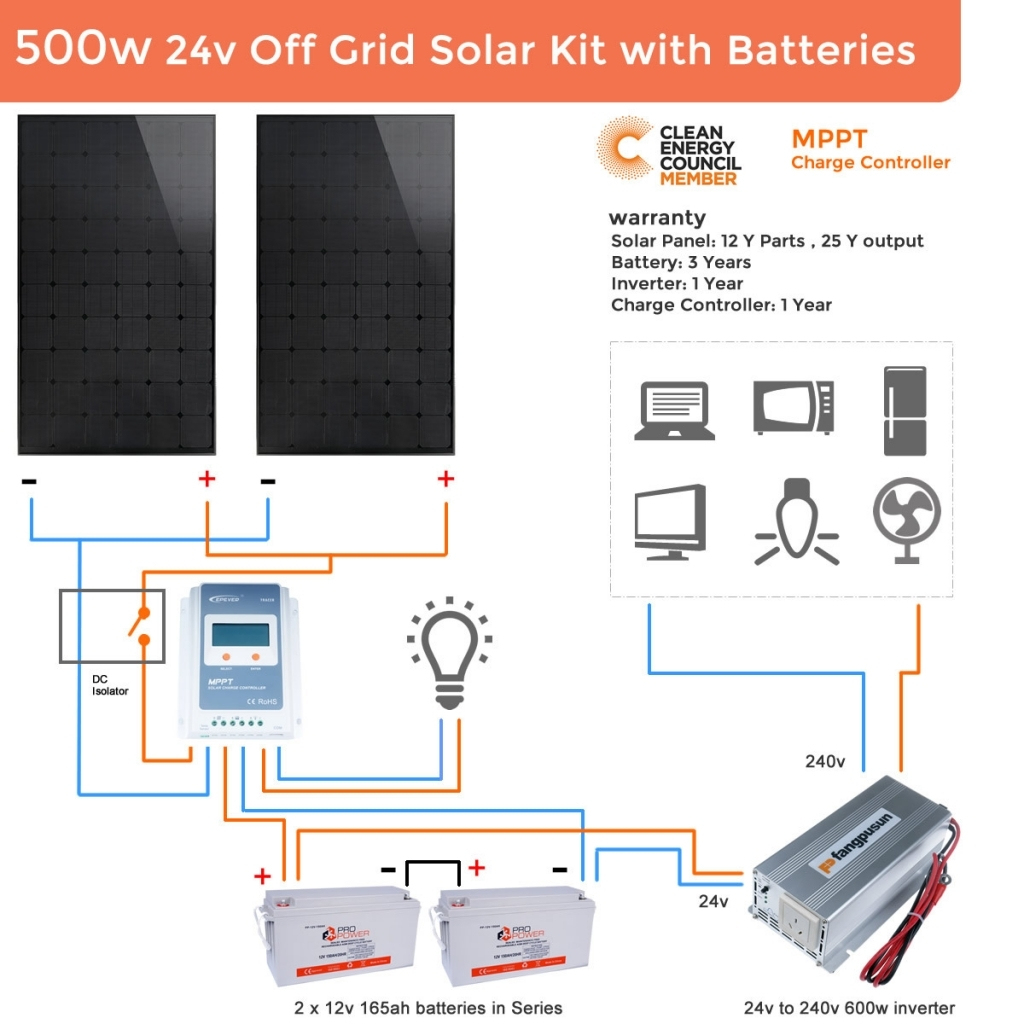
“Grid-connected solar wiring for home”
Introduction to Grid-Connected Solar Systems
A grid-connected solar system, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) system, uses solar panels to generate electricity from sunlight. The generated electricity is then fed into the electrical grid, which supplies power to the home. When the solar system produces more electricity than the home consumes, the excess energy is sold back to the grid, earning the homeowner credits or revenue. Grid-connected solar systems are designed to operate in parallel with the electrical grid, allowing homeowners to draw energy from the grid when the solar system is not producing enough electricity.
Components of a Grid-Connected Solar System
A typical grid-connected solar system consists of the following components:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight into electrical energy. They are usually mounted on the roof or in a sunny area of the property.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC (direct current) electricity generated by the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is compatible with the electrical grid.
- Mounting System: This includes the racks, clamps, and other hardware used to secure the solar panels to the roof or ground.
- Wiring and Connectors: These connect the solar panels, inverter, and other components to the electrical grid.
- Electrical Panel: This is the main electrical distribution panel that connects the solar system to the grid and distributes power to the home.
- Net Meter: This device measures the amount of electricity produced by the solar system and the amount consumed by the home, allowing the homeowner to track their energy production and consumption.

Design Considerations for Grid-Connected Solar Wiring
When designing a grid-connected solar system, several factors must be considered to ensure safe and efficient operation:
- System Size and Configuration: The size and configuration of the solar system will depend on the homeowner’s energy needs and available space. A larger system will require more solar panels, inverters, and wiring.
- Voltage and Current: The voltage and current of the solar system must be compatible with the electrical grid and the home’s electrical panel.
- Wire Sizing and Rating: The wire size and rating must be sufficient to handle the current and voltage of the solar system, as well as the temperatures and environmental conditions of the installation site.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential to ensure the safety of the solar system and the home’s electrical system.
- Electrical Codes and Standards: The solar system must comply with local electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electric Code (NEC) in the United States.
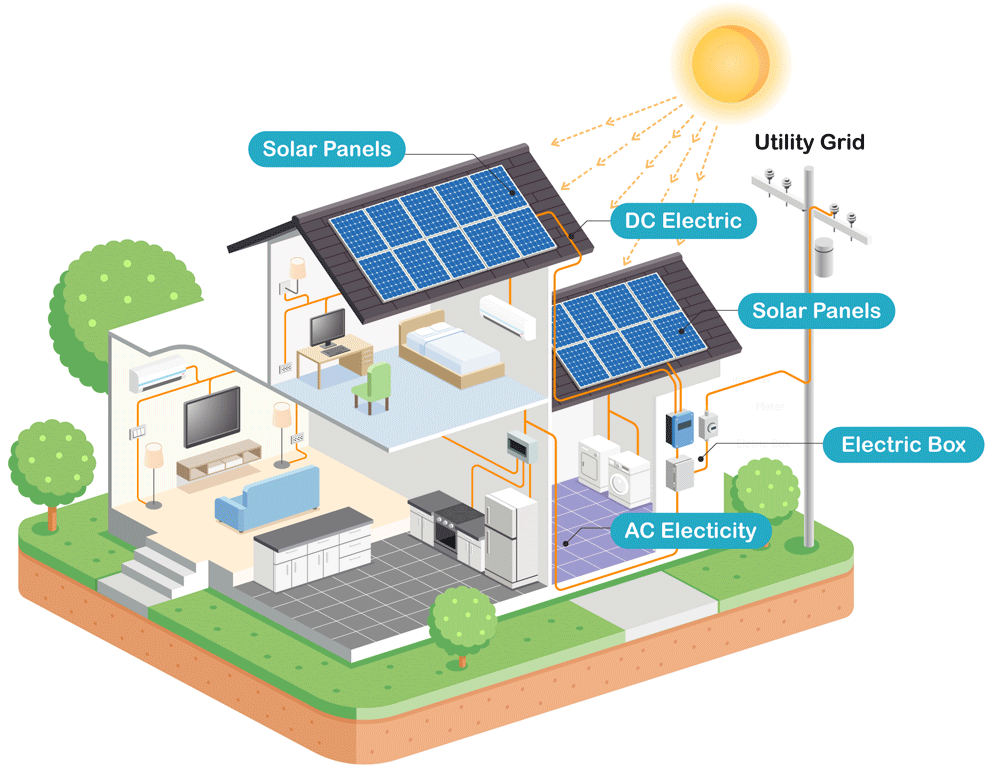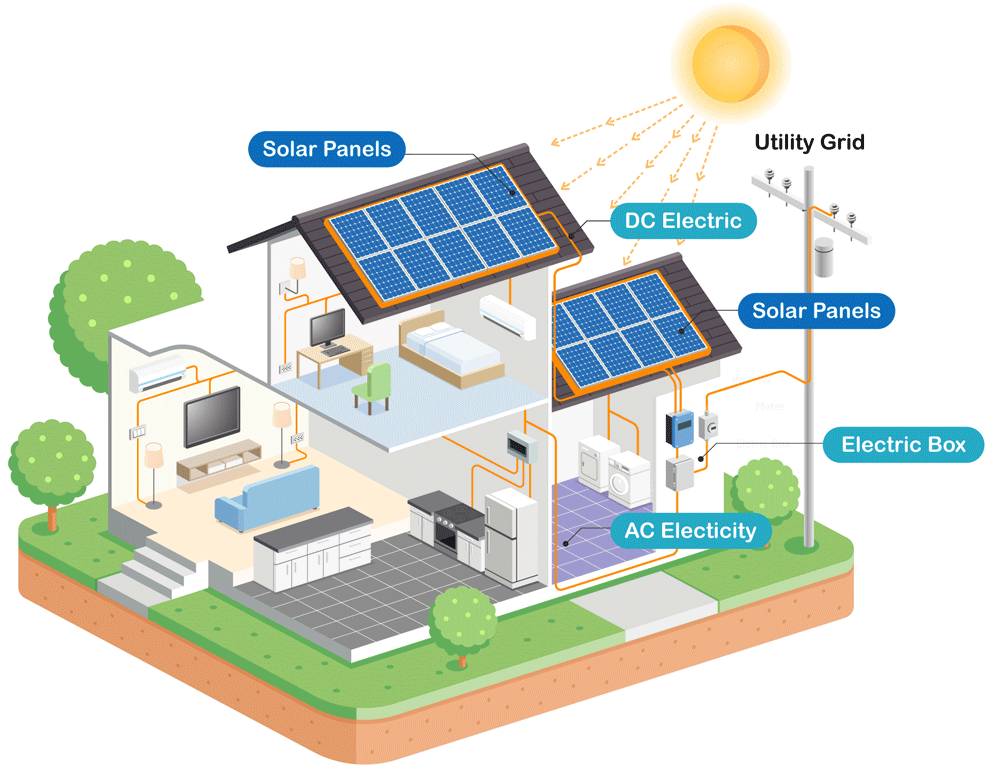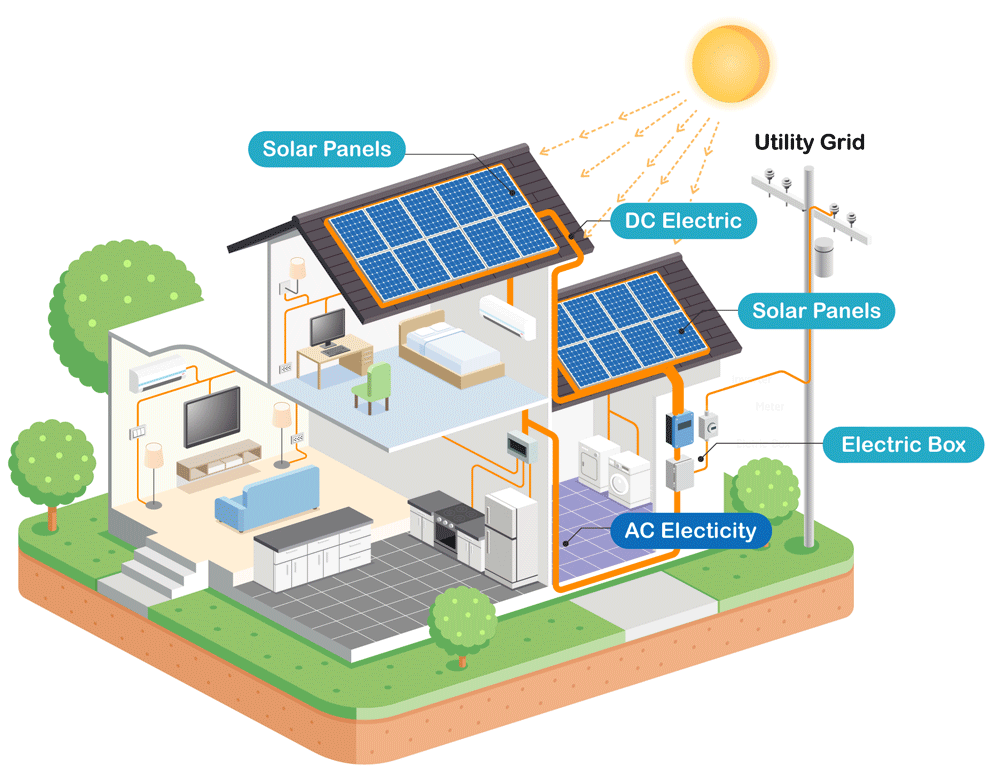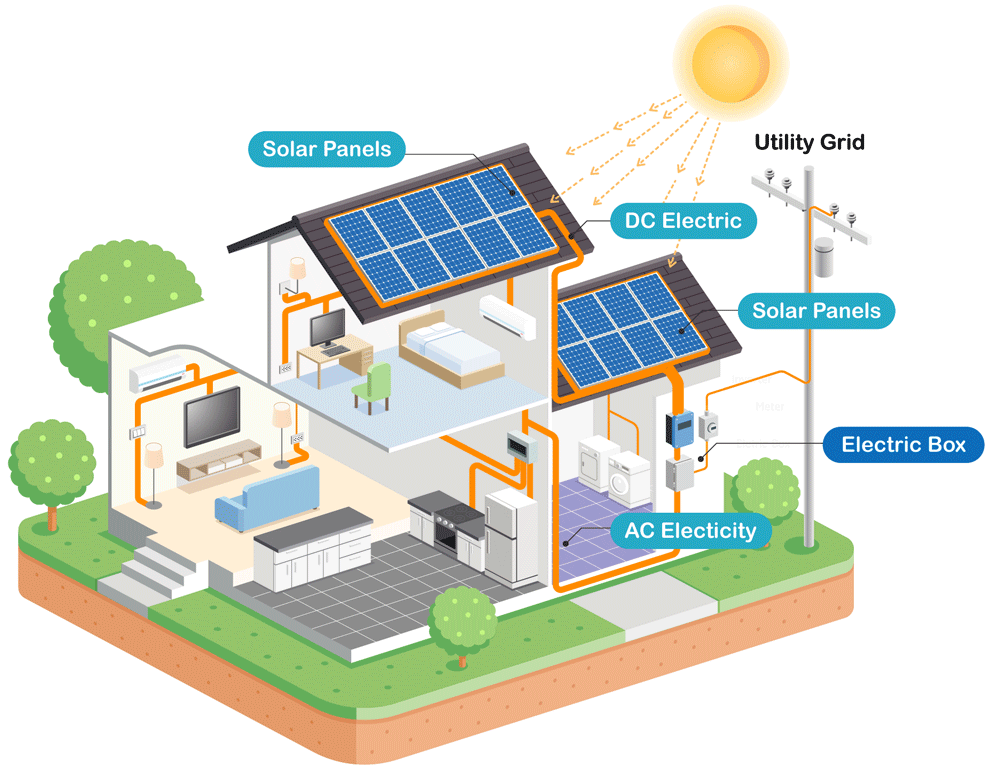

Wiring and Connection Requirements
The wiring and connection requirements for a grid-connected solar system will depend on the system size and configuration, as well as local electrical codes and standards. Some common requirements include:
- DC Wiring: The DC wiring between the solar panels and the inverter must be sized and rated to handle the current and voltage of the solar system.
- AC Wiring: The AC wiring between the inverter and the electrical panel must be sized and rated to handle the current and voltage of the solar system.
- Grounding and Bonding: The solar system must be grounded and bonded to the home’s electrical panel and grounding system.
- Connectors and Fittings: The connectors and fittings used to connect the solar panels, inverter, and other components must be compatible with the wiring and components used in the system.
- Labeling and Marking: The wiring and components must be labeled and marked to identify their purpose and function.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
When installing a grid-connected solar system, several safety precautions and considerations must be taken to ensure the safety of the homeowner, installers, and the electrical grid:
- Electrical Shock: The solar system must be designed and installed to prevent electrical shock and ensure the safety of the homeowner and installers.
- Fire Risk: The solar system must be designed and installed to minimize the risk of fire, including the use of fire-resistant materials and proper ventilation.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential to ensure the safety of the solar system and the home’s electrical system.
- Arc Fault Protection: The solar system must be designed and installed to prevent arc faults, which can cause fires and electrical shock.
- Regular Maintenance: The solar system must be regularly maintained to ensure safe and efficient operation, including cleaning, inspection, and repair of components as needed.
Installation and Commissioning
The installation and commissioning of a grid-connected solar system require careful attention to detail and adherence to local electrical codes and standards. Some common steps involved in the installation and commissioning process include:
- Site Assessment: The installation site must be assessed to ensure that it is suitable for the solar system, including the availability of sunlight and the condition of the roof or mounting structure.
- Component Installation: The solar panels, inverter, and other components must be installed and connected according to the manufacturer’s instructions and local electrical codes and standards.
- Wiring and Connection: The wiring and connections must be made according to the system design and local electrical codes and standards.
- Grounding and Bonding: The solar system must be grounded and bonded to the home’s electrical panel and grounding system.
- Testing and Commissioning: The solar system must be tested and commissioned to ensure that it is operating safely and efficiently.
Conclusion
Grid-connected solar wiring for homes requires careful attention to detail and adherence to local electrical codes and standards. By following the design considerations, wiring and connection requirements, safety precautions, and installation and commissioning procedures outlined in this article, homeowners can ensure a safe and efficient solar system that provides reliable and renewable energy for years to come. As the demand for grid-connected solar systems continues to grow, it is essential to prioritize safety, efficiency, and compliance with local regulations to ensure the long-term success of these systems.