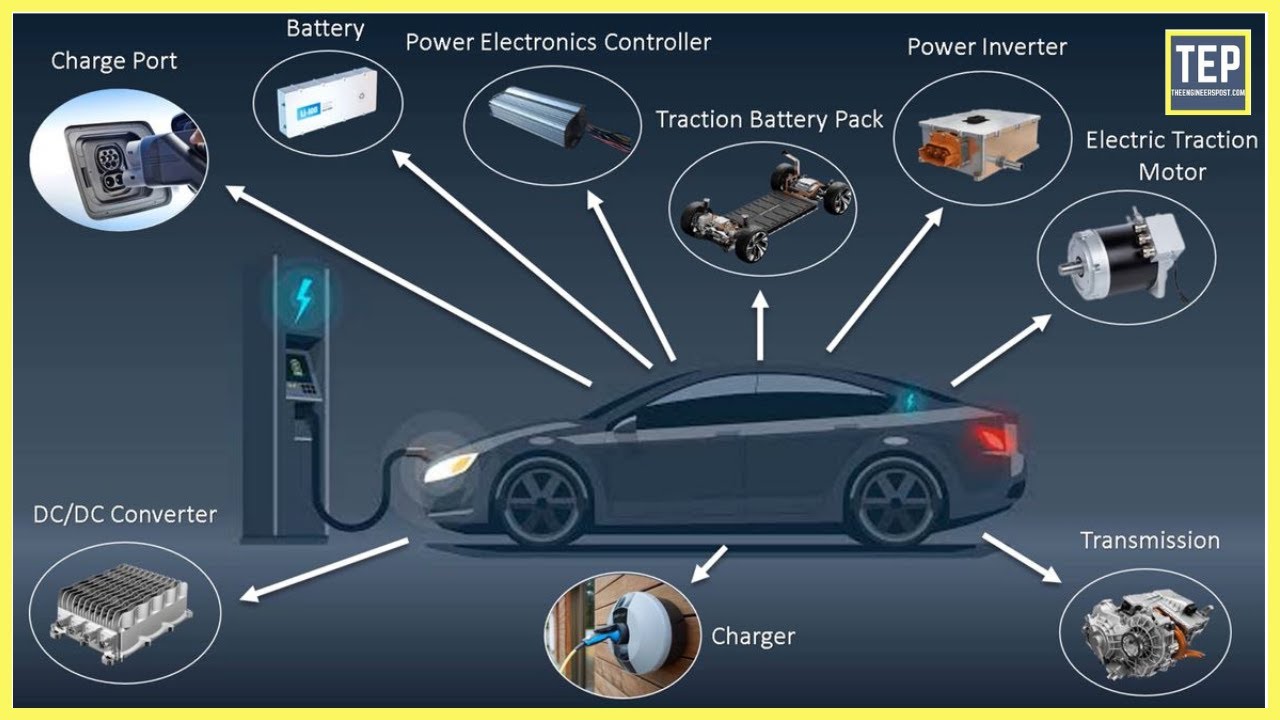
With governments setting targets to phase out internal combustion engines and manufacturers investing heavily in EV technology, the demand for electric vehicles is on the rise. But have you ever wondered what makes an electric vehicle tick? In this article, we will delve into the main components of an electric vehicle, exploring their functions, benefits, and the role they play in making EVs a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
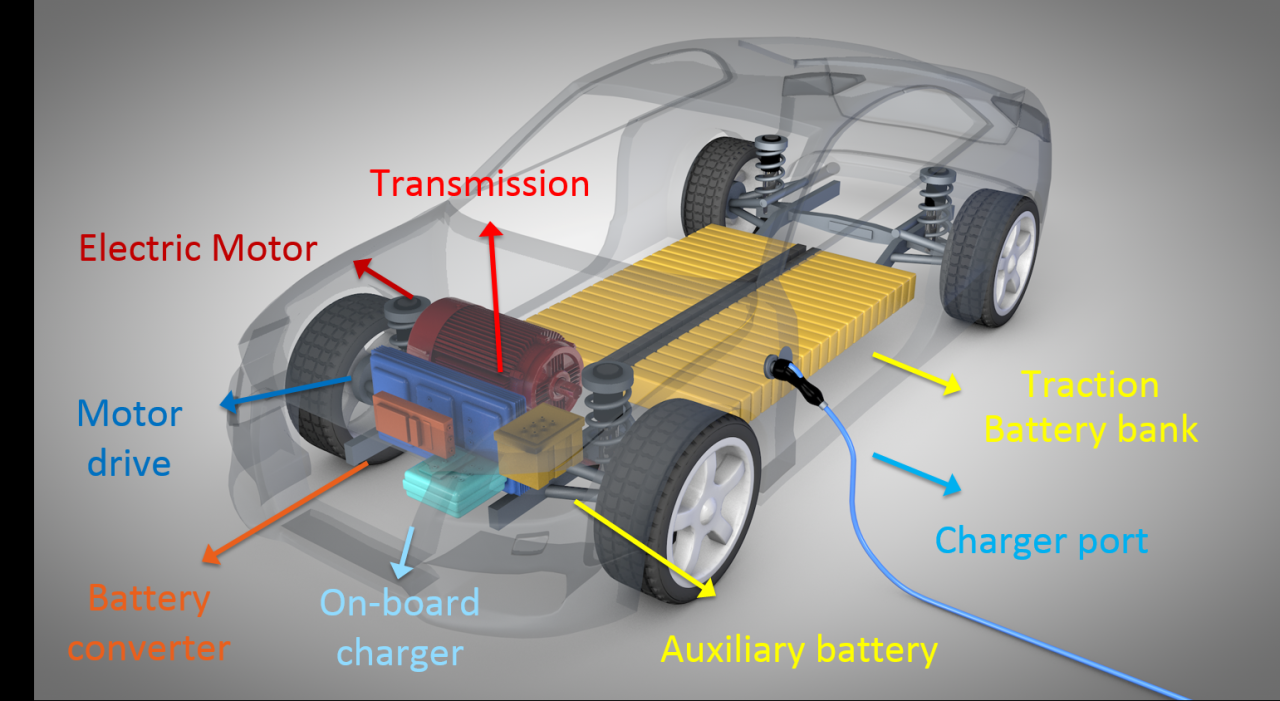
1. Electric Motor
The electric motor is the heart of an electric vehicle, responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. There are several types of electric motors used in EVs, including:
- DC Brushless Motor: This type of motor uses a DC power source and is commonly used in hybrid and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles.
- AC Induction Motor: This type of motor uses an AC power source and is commonly used in battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
- Permanent Magnet Motor: This type of motor uses a permanent magnet as the rotor and is commonly used in high-performance EVs.
Electric motors have several advantages over traditional internal combustion engines, including higher efficiency, lower maintenance, and reduced noise pollution. They also provide instant torque, making EVs accelerate quickly and smoothly.
2. Battery Pack
The battery pack is a critical component of an electric vehicle, providing the energy storage needed to power the electric motor. Battery packs are typically made up of multiple individual battery cells, which are connected in series and parallel to provide the required voltage and capacity.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are the most common type of battery used in EVs, offering high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rates.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries: These batteries are less common in EVs but are still used in some hybrid vehicles.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: These batteries are rarely used in EVs due to their low energy density and short cycle life.
Battery packs are designed to be durable and long-lasting, with some manufacturers offering warranties of up to 8 years or 100,000 miles. However, battery degradation over time can affect an EV's range and performance.
3. Power Electronics
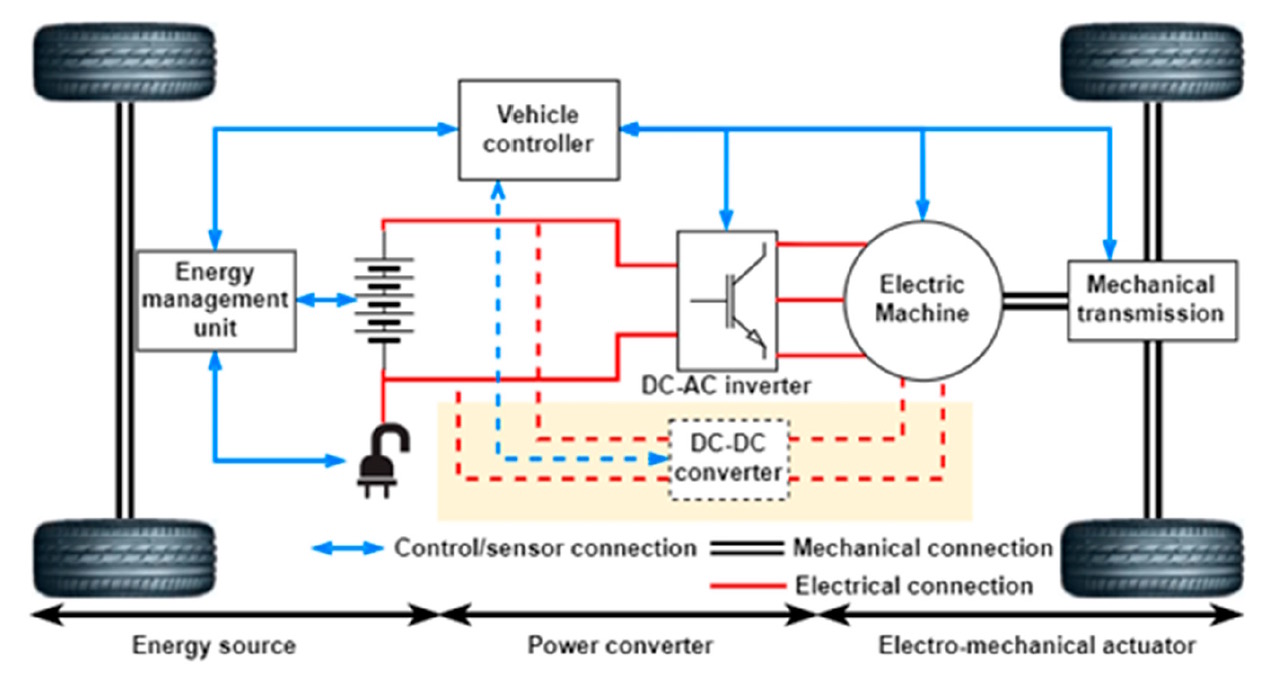
Power electronics play a crucial role in controlling the flow of electrical energy between the battery pack, electric motor, and other components of the vehicle. The main power electronics components include:
- Inverter: This component converts DC power from the battery pack into AC power for the electric motor.
- Converter: This component converts AC power from the electric motor into DC power for the battery pack during regenerative braking.
- Charging System: This component controls the flow of energy during charging, ensuring the battery pack is charged safely and efficiently.
Power electronics are designed to be highly efficient and reliable, with some manufacturers using advanced technologies such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) to reduce losses and improve performance.
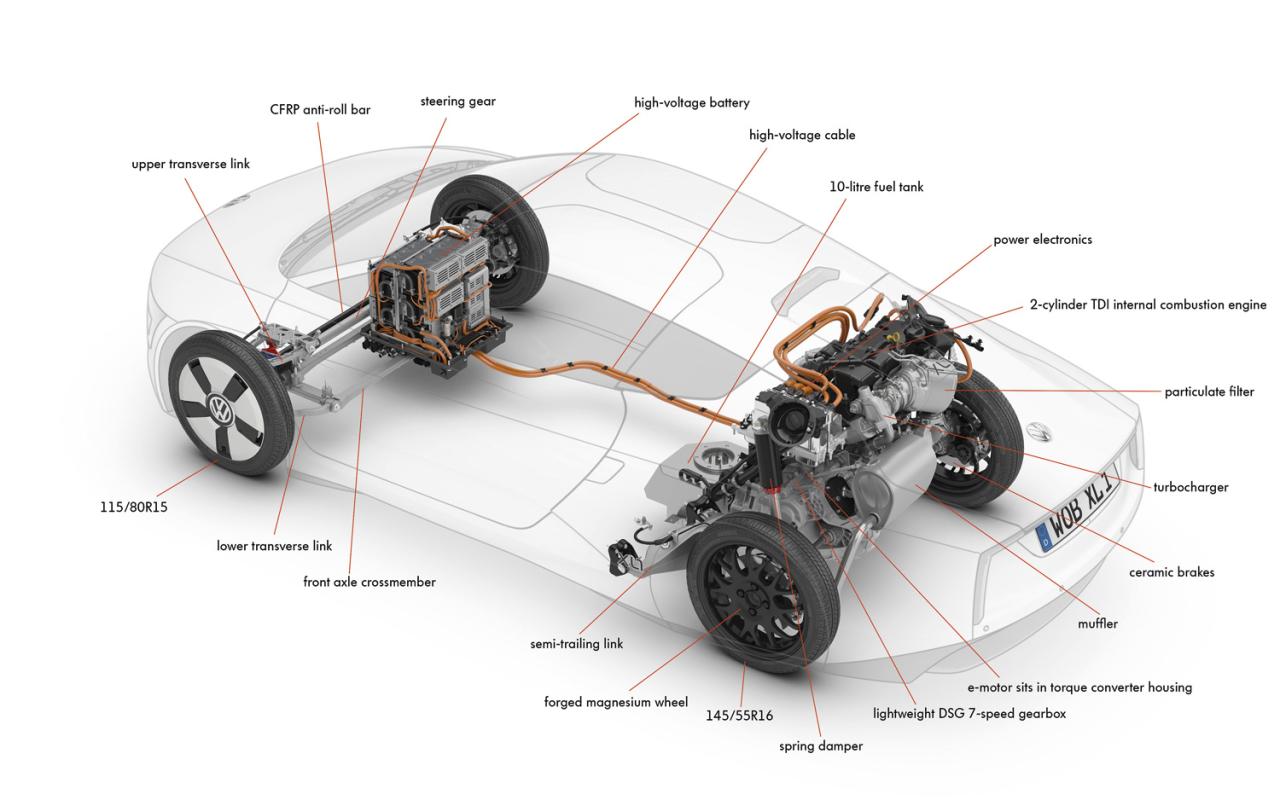
4. Transmission and Drivetrain
The transmission and drivetrain of an electric vehicle are designed to be efficient and reliable, with some EVs using a single-speed or multi-speed transmission. The main components include:
- Transmission: This component transmits power from the electric motor to the wheels, with some EVs using a fixed gear ratio and others using a variable gear ratio.
- Differential: This component enables the wheels to rotate at different speeds, improving traction and stability.
- Driveshaft: This component connects the transmission to the wheels, transmitting power and torque.
The transmission and drivetrain of an EV are designed to be compact and lightweight, with some manufacturers using advanced materials and technologies to reduce energy losses and improve efficiency.
5. Charging System
The charging system of an electric vehicle is designed to be safe, efficient, and convenient, with several charging options available:
- Level 1 Charging: This type of charging uses a standard 120V household outlet and is suitable for low-mileage drivers.
- Level 2 Charging: This type of charging uses a 240V charging station and is suitable for most EV owners.
- DC Fast Charging: This type of charging uses a high-power DC charging station and can charge an EV to 80% in under 30 minutes.
Charging systems are designed to be user-friendly, with many EVs offering advanced charging features such as scheduled charging, remote charging, and charging station mapping.
6. Battery Management System (BMS)
The battery management system (BMS) is a critical component of an electric vehicle, responsible for monitoring and controlling the battery pack's state of charge, state of health, and temperature. The BMS ensures the battery pack operates within a safe and efficient range, preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating.
- Cell Balancing: This function ensures that all battery cells are charged and discharged evenly, preventing any single cell from becoming overcharged or undercharged.
- State of Charge (SoC) Estimation: This function estimates the battery pack's state of charge, enabling the vehicle to provide accurate range estimates and prevent over-discharging.
- Thermal Management: This function monitors and controls the battery pack's temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
The BMS is a sophisticated system that uses advanced algorithms and sensors to monitor and control the battery pack, ensuring the EV operates safely and efficiently.
7. Electrical Architecture
The electrical architecture of an electric vehicle is designed to be efficient, reliable, and scalable, with several components working together to provide power to the vehicle's systems:
- High-Voltage System: This system provides power to the electric motor, transmission, and other high-voltage components.
- Low-Voltage System: This system provides power to the vehicle's accessories, such as the lights, radio, and wipers.
- Communication Network: This network enables communication between the vehicle's systems, including the BMS, transmission, and electric motor.
The electrical architecture of an EV is designed to be modular and flexible, with many manufacturers using standardized components and interfaces to simplify production and reduce costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the main components of an electric vehicle work together to provide a safe, efficient, and enjoyable driving experience. From the electric motor to the battery pack, power electronics, transmission, and charging system, each component plays a critical role in making EVs a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more efficient, reliable, and affordable electric vehicles on the road, helping to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and create a more sustainable transportation system for the future.
Future Outlook
As the world continues to shift towards electrification, we can expect to see significant advancements in electric vehicle technology. Some of the trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of EVs include:
- Improved Battery Technology: Advances in battery technology are expected to improve energy density, reduce costs, and increase range.
- Increased Adoption of Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles are likely to play a significant role in the future of transportation, with many manufacturers investing heavily in autonomous EV technology.
- Growing Demand for Sustainable Energy: As concern for the environment grows, there will be an increasing demand for sustainable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to charge EVs.
Overall, the future of electric vehicles looks bright, with many manufacturers, governments, and consumers working together to create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the world of electric vehicles, helping to shape a cleaner, more efficient, and more enjoyable driving experience for generations to come.