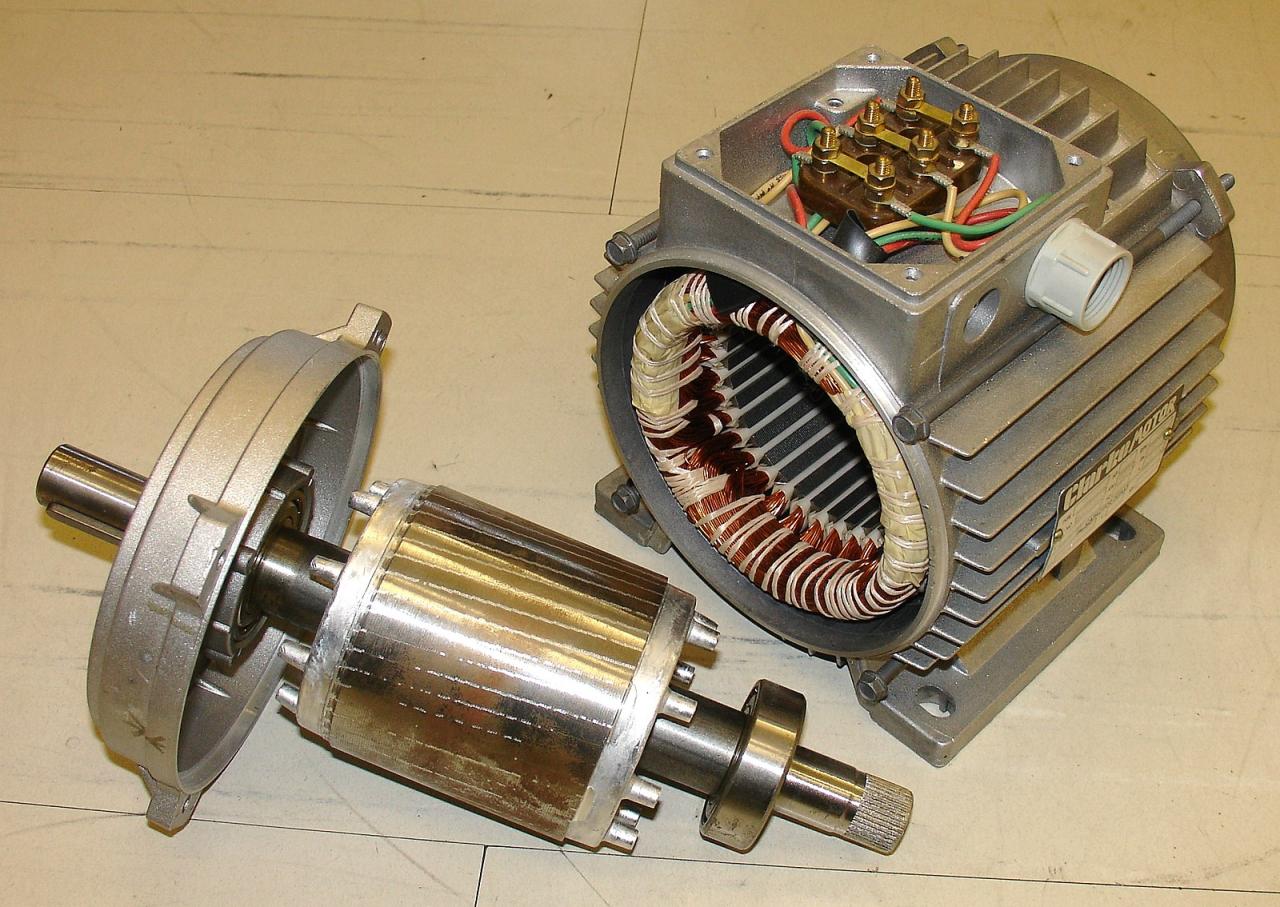
The layout of these components plays a crucial role in determining the overall efficiency, performance, and reliability of the vehicle. In this article, we will delve into the world of electric vehicle powertrain component layout, exploring the different configurations, advantages, and challenges associated with each.
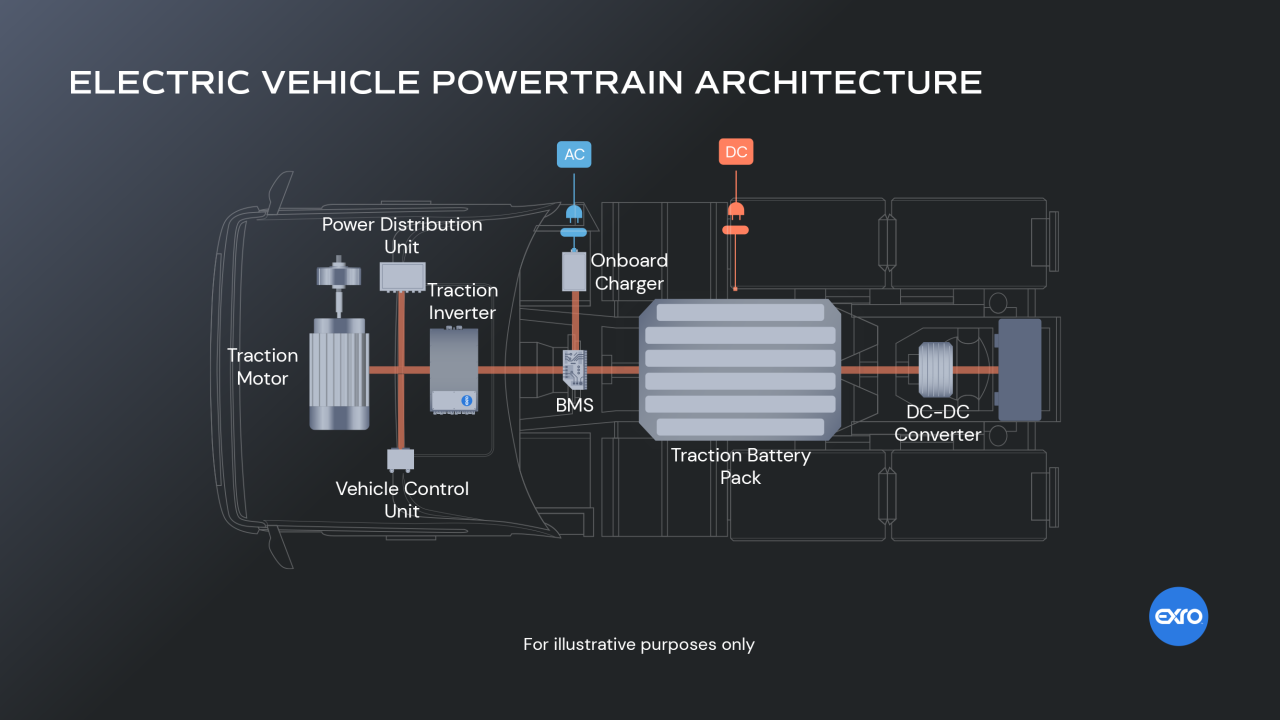
Introduction to Electric Vehicle Powertrains
Electric vehicles use electric motors, powered by batteries, to propel the vehicle. The powertrain consists of several key components, including:
- Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle.
- Battery Pack: Stores electrical energy to power the motor.
- Power Electronics: Controls the flow of electrical energy between the battery and motor.
- Transmission: Transfers mechanical energy from the motor to the wheels.
- Thermal Management System: Regulates the temperature of the powertrain components.
Powertrain Component Layout Configurations
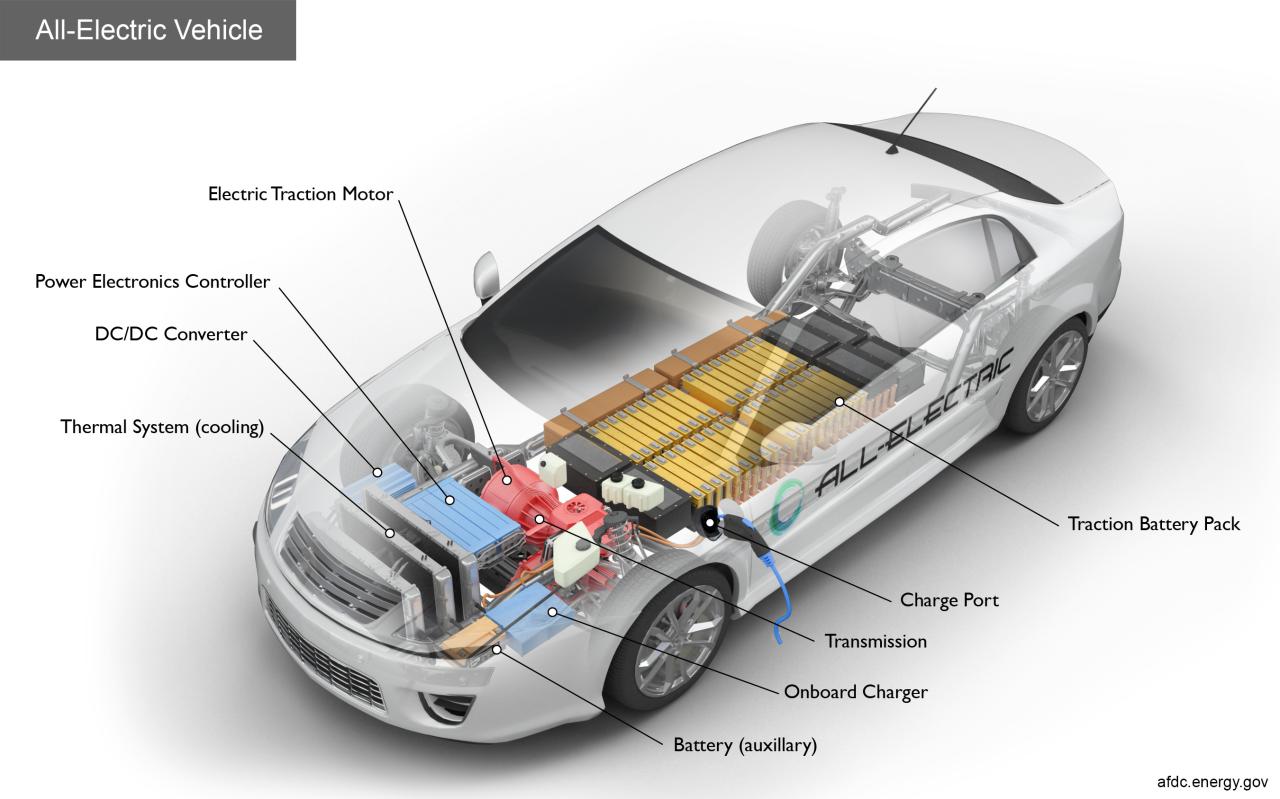
There are several powertrain component layout configurations used in electric vehicles, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common configurations include:
- Central Motor Configuration: In this configuration, the electric motor is located at the center of the vehicle, with the battery pack and power electronics located nearby. This configuration is commonly used in rear-wheel drive (RWD) and all-wheel drive (AWD) vehicles.
- Axle-Mounted Motor Configuration: In this configuration, the electric motor is integrated into the axle, with the battery pack and power electronics located elsewhere in the vehicle. This configuration is commonly used in front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles.
- Distributed Motor Configuration: In this configuration, multiple electric motors are used, each located near a wheel or axle. This configuration is commonly used in high-performance and AWD vehicles.
- Modular Powertrain Configuration: In this configuration, the powertrain components are packaged into a single module, which can be easily integrated into different vehicle platforms. This configuration is commonly used in vehicle platforms designed for multiple powertrain options.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Configuration
Each powertrain component layout configuration has its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the key benefits and drawbacks include:
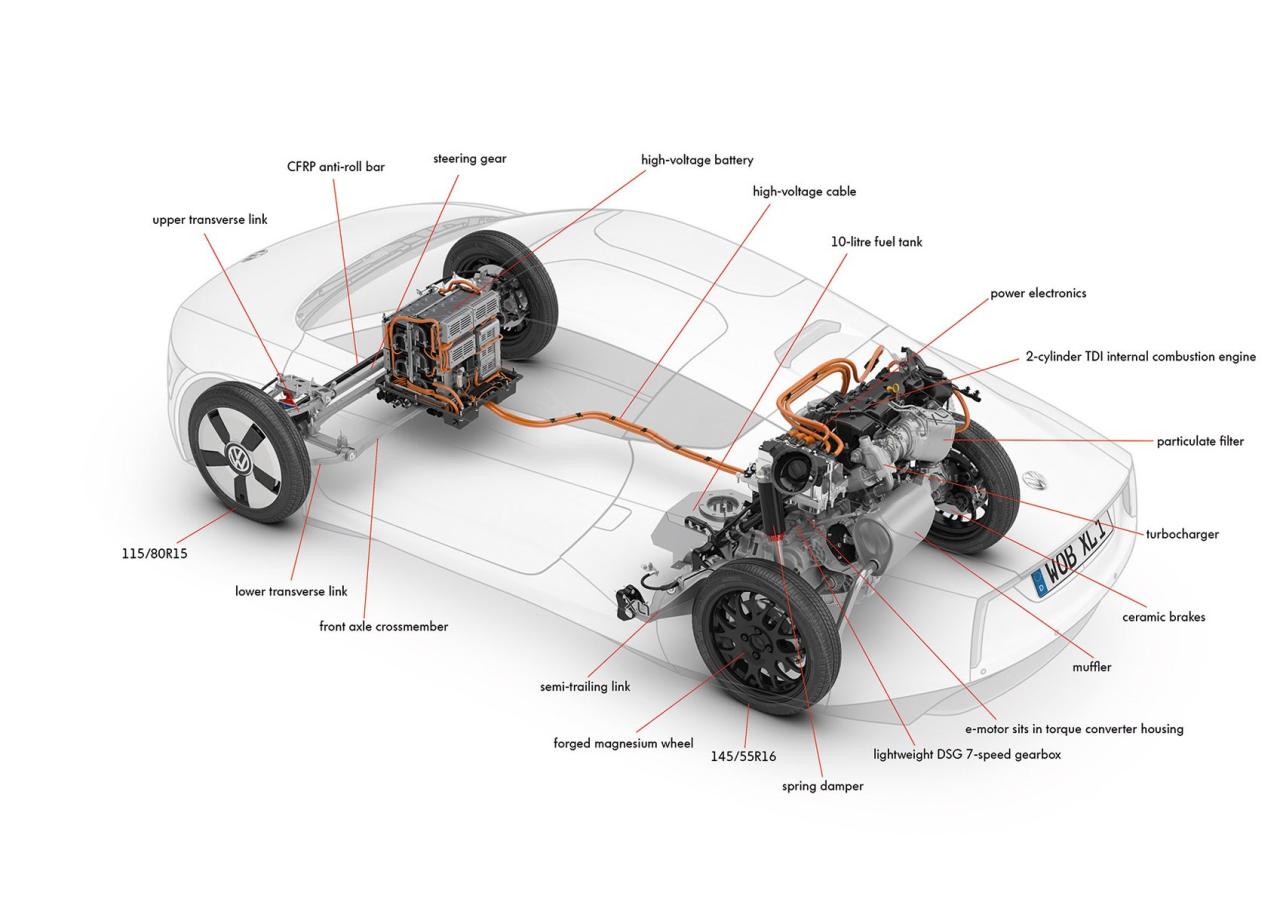
- Central Motor Configuration:
- Advantages: Simple and compact design, easy to package, and low cost.
- Disadvantages: Limited flexibility, potential for motor noise and vibration, and heat management challenges.
- Axle-Mounted Motor Configuration:
- Advantages: Improved packaging, reduced motor noise and vibration, and enhanced thermal management.
- Disadvantages: Increased complexity, higher cost, and potential for reduced motor efficiency.
- Distributed Motor Configuration:
- Advantages: Improved traction, enhanced performance, and increased flexibility.
- Disadvantages: Increased complexity, higher cost, and potential for reduced motor efficiency.
- Modular Powertrain Configuration:
- Advantages: Easy integration, reduced development time and cost, and improved flexibility.
- Disadvantages: Potential for reduced performance, increased weight, and thermal management challenges.
Thermal Management System Integration
The thermal management system (TMS) plays a critical role in regulating the temperature of the powertrain components. The TMS consists of several components, including:
- Coolant: A liquid or gas used to transfer heat from the powertrain components to the TMS.
- Heat Exchanger: A device used to transfer heat from the coolant to the ambient air or a secondary coolant loop.
- Pumps and Fans: Used to circulate the coolant and provide airflow to the heat exchanger.
The TMS can be integrated into the powertrain component layout in several ways, including:
- Air-Cooled TMS: Uses airflow to cool the powertrain components.
- Liquid-Cooled TMS: Uses a liquid coolant to cool the powertrain components.
- Hybrid TMS: Combines air-cooled and liquid-cooled TMS components.
Challenges and Considerations
The powertrain component layout configuration can have a significant impact on the overall performance, efficiency, and reliability of the vehicle. Some of the key challenges and considerations include:
- Packaging and Integration: The powertrain components must be packaged and integrated into the vehicle platform, while minimizing weight, cost, and complexity.
- Thermal Management: The TMS must be designed to regulate the temperature of the powertrain components, while minimizing weight, cost, and complexity.
- Noise and Vibration: The powertrain components can generate noise and vibration, which must be mitigated to ensure a comfortable and quiet ride.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility: The powertrain components can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI), which must be mitigated to ensure proper operation of the vehicle systems.
Conclusion
The electric vehicle powertrain component layout is a complex system that requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including packaging, thermal management, noise and vibration, and electromagnetic compatibility. The different powertrain component layout configurations each have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of configuration depends on the specific vehicle application and requirements. By understanding the challenges and considerations associated with the powertrain component layout, vehicle manufacturers can design and develop more efficient, reliable, and high-performance electric vehicles.
Future Developments
As the electric vehicle market continues to evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative powertrain component layout configurations emerge. Some of the potential future developments include:
- Advanced Materials and Designs: New materials and designs, such as carbon fiber and advanced composites, can be used to reduce weight and improve packaging.
- Modular and Scalable Designs: Modular and scalable designs can be used to simplify the development and production process, while improving flexibility and reducing cost.
- Thermal Management System Advances: Advances in TMS technology, such as more efficient heat exchangers and pumps, can be used to improve thermal management and reduce weight and cost.
- Autonomous and Connected Vehicle Technologies: Autonomous and connected vehicle technologies can be integrated into the powertrain component layout, enabling new features and capabilities, such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
By embracing these future developments and continuing to innovate and improve the powertrain component layout, the electric vehicle industry can drive growth, efficiency, and sustainability, while providing customers with more efficient, reliable, and high-performance vehicles.