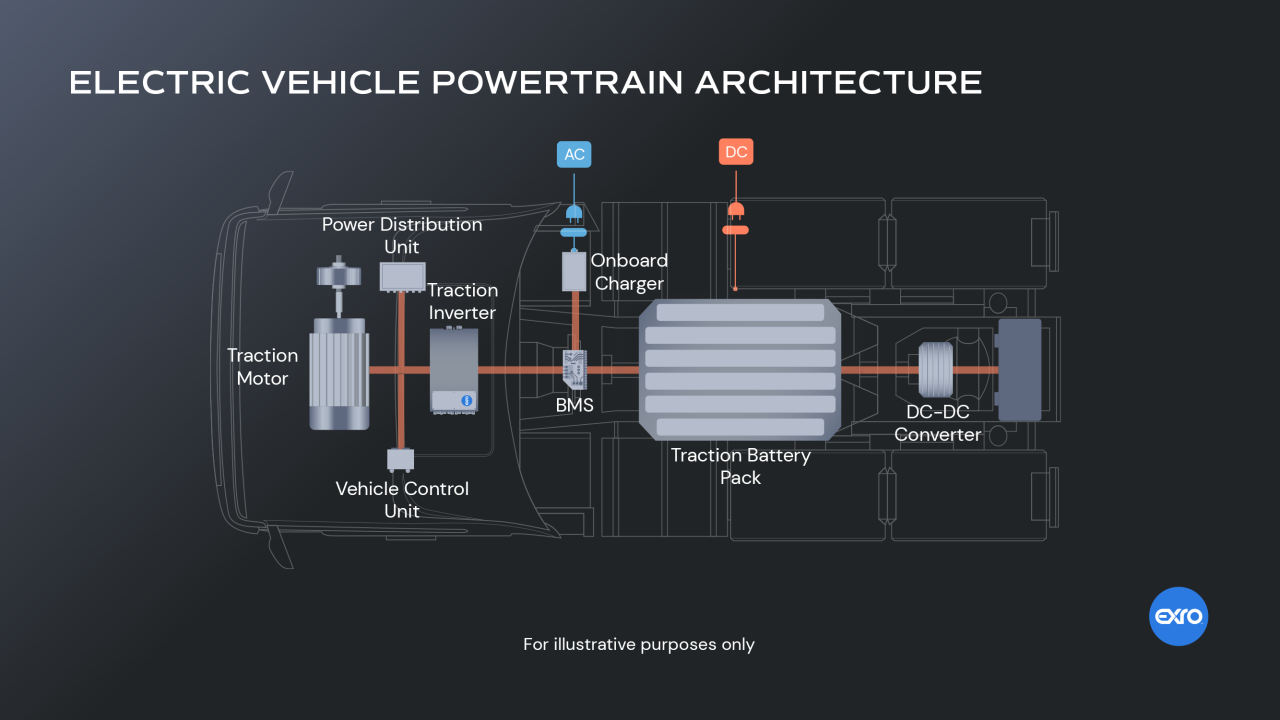
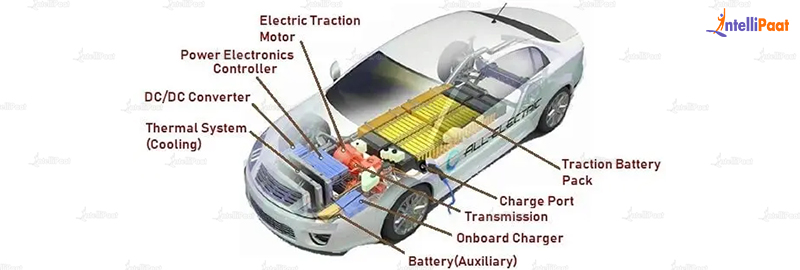
With their zero-emission capabilities and lower operating costs, EVs are becoming increasingly popular among consumers. However, the technology behind these vehicles is complex and involves several major components that work together to provide a seamless driving experience. In this article, we will delve into the major components of electric vehicles, exploring their functions, advantages, and challenges.
1. Electric Motor
The electric motor is the heart of an electric vehicle, responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. EVs use one or more electric motors, which are typically three-phase induction motors or permanent magnet motors. These motors are powered by an electric current from the battery pack and use electromagnetic forces to generate torque. The electric motor is more efficient and has a higher power-to-weight ratio compared to traditional internal combustion engines.
There are several types of electric motors used in EVs, including:
- Induction Motor (IM): This is the most common type of electric motor used in EVs, known for its simplicity, reliability, and low cost.
- Permanent Magnet Motor (PMM): This type of motor uses permanent magnets to generate the magnetic field, providing higher efficiency and power density.
- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM): This motor uses a switched reluctance design, which offers high efficiency and reliability at a lower cost.
2. Battery Pack
The battery pack is a crucial component of an electric vehicle, responsible for storing the electrical energy used to power the motor. EVs use rechargeable batteries, typically lithium-ion batteries, which offer high energy density and long cycle life. The battery pack consists of multiple individual battery cells, which are connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
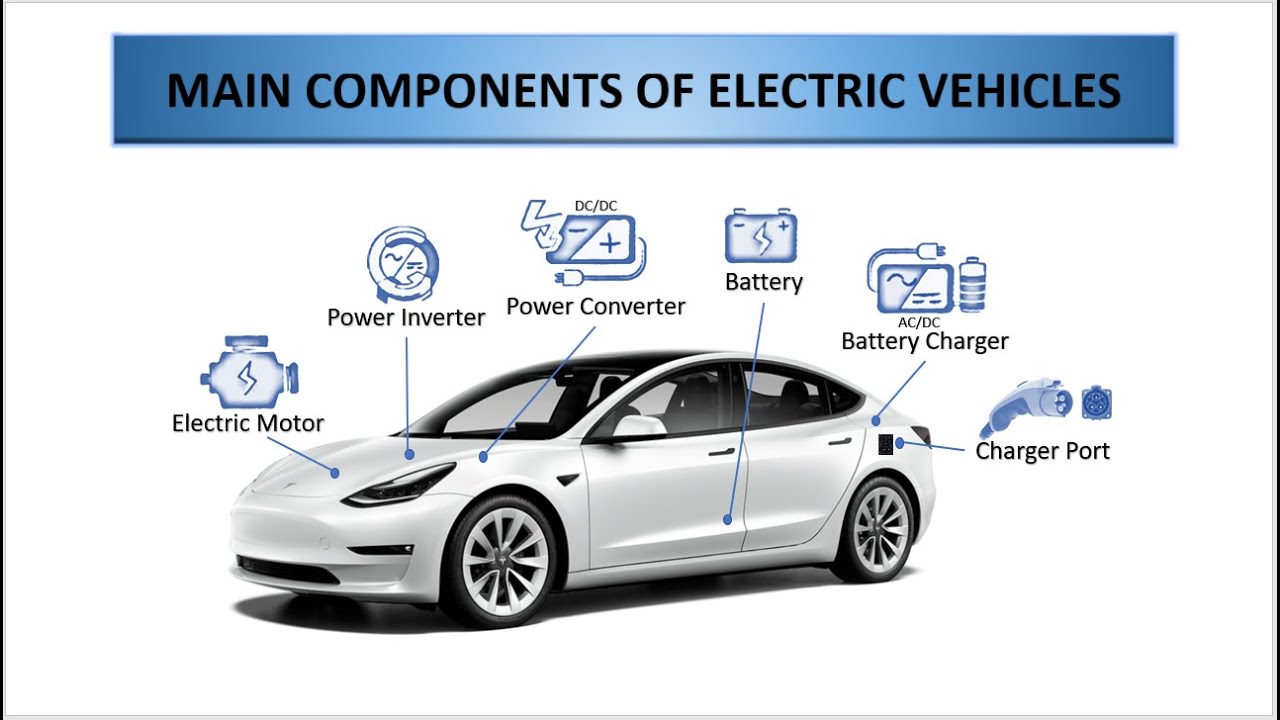
The battery pack plays a critical role in determining the range and performance of an EV. Factors such as battery chemistry, cell design, and thermal management can significantly impact the overall efficiency and lifespan of the battery pack. Advancements in battery technology have led to improved energy density, reduced costs, and increased adoption of EVs.
3. Power Electronics
Power electronics play a vital role in controlling the flow of electrical energy between the battery pack, electric motor, and other components of the EV. The power electronics system consists of several components, including:
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC power from the battery pack into AC power for the electric motor.
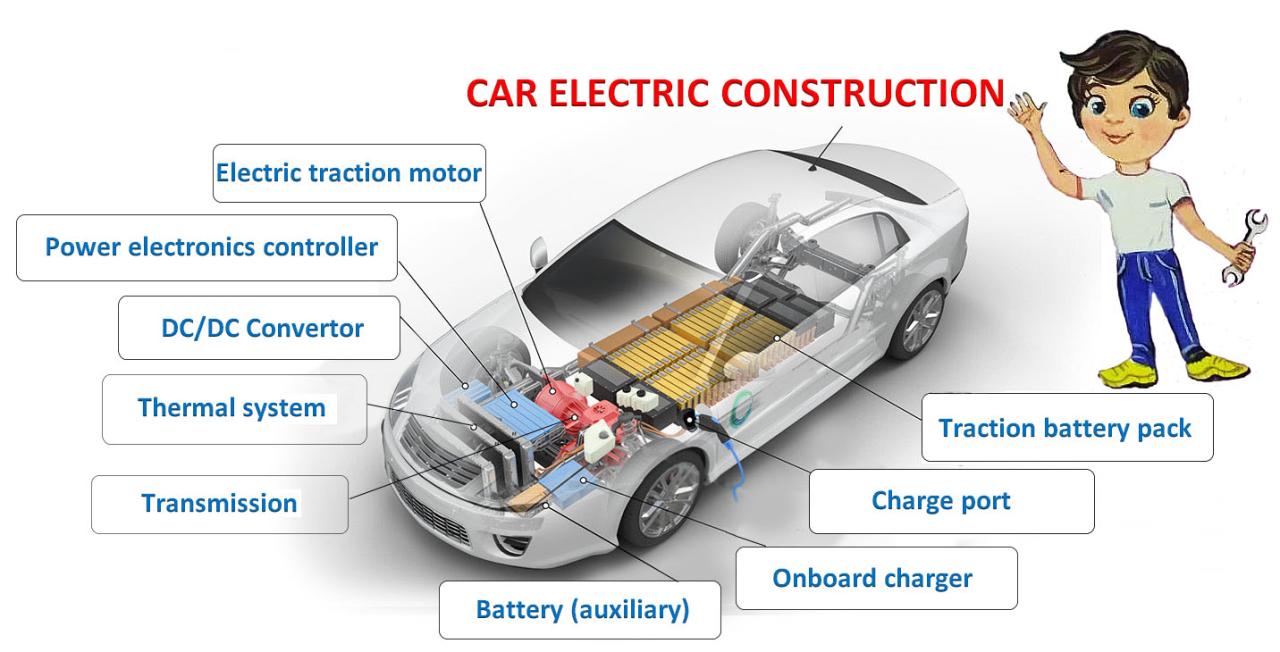
- DC-DC Converter: The DC-DC converter steps down the high voltage from the battery pack to a lower voltage required by the vehicle's onboard systems.
- Charging System: The charging system manages the flow of energy from the charging station to the battery pack.
Power electronics are responsible for optimizing energy efficiency, reducing power losses, and ensuring safe and reliable operation of the EV.
4. Transmission and Gearbox
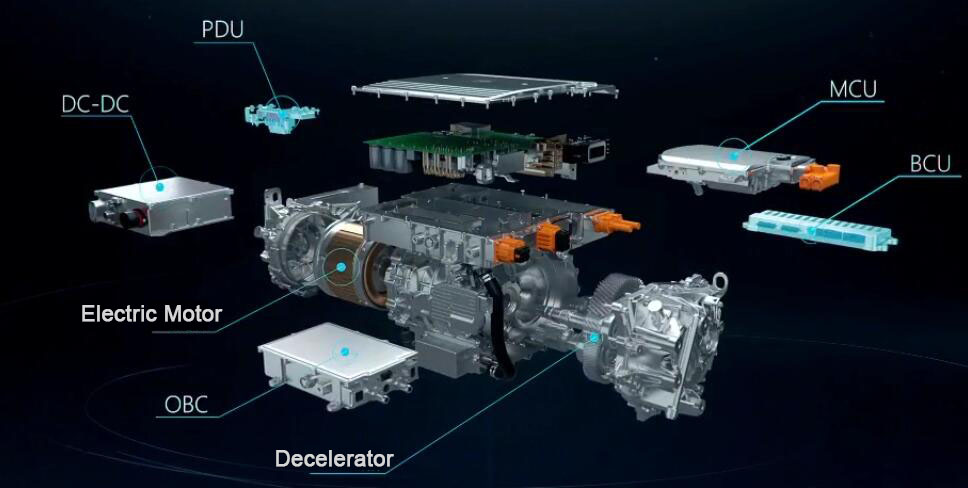
While electric vehicles do not require a traditional transmission system like internal combustion engines, some EVs use a gearbox or transmission to optimize the performance and efficiency of the electric motor. The transmission system in an EV typically consists of a single-speed or multi-speed gearbox, which helps to:
- Optimize Motor Speed: The gearbox helps to maintain the electric motor within its optimal speed range, improving efficiency and reducing wear and tear.
- Improve Acceleration: The transmission system enables the EV to accelerate more quickly and smoothly, especially from a standstill.
However, some EVs, like the Tesla Model S, use a single-speed gearbox, which simplifies the design and reduces energy losses.
5. Charging System
The charging system is a critical component of an electric vehicle, enabling the vehicle to recharge its battery pack from an external power source. The charging system consists of:
- Onboard Charger: The onboard charger converts the AC power from the charging station to DC power, which is then used to charge the battery pack.
- Charging Port: The charging port is the interface between the vehicle and the charging station, providing a safe and secure connection for energy transfer.
There are several types of charging systems used in EVs, including:
- Level 1 (120V): This is the slowest and most basic charging method, using a standard household outlet.
- Level 2 (240V): This charging method uses a dedicated 240V charging station, providing faster charging times.
- DC Fast Charging: This is the fastest charging method, using a high-power DC charging station to recharge the battery pack to 80% in under 30 minutes.
6. Thermal Management System
The thermal management system is responsible for maintaining the optimal operating temperature of the electric motor, battery pack, and other components of the EV. The system uses a combination of cooling and heating elements to:
- Cool the Battery Pack: The thermal management system helps to prevent overheating of the battery pack, which can reduce its lifespan and performance.
- Regulate Motor Temperature: The system maintains the optimal temperature of the electric motor, ensuring efficient operation and preventing damage.
The thermal management system is essential for ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and safety of the EV.
7. Control Systems
The control systems in an electric vehicle are responsible for managing the flow of energy and information between the various components. The control systems include:
- Vehicle Control Unit (VCU): The VCU is the central computer that manages the EV's systems, including the electric motor, battery pack, and charging system.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors and controls the battery pack, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
The control systems play a critical role in optimizing the performance, efficiency, and safety of the EV.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the major components of electric vehicles are complex and interconnected systems that work together to provide a seamless driving experience. The electric motor, battery pack, power electronics, transmission and gearbox, charging system, thermal management system, and control systems all play critical roles in optimizing the performance, efficiency, and safety of EVs. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements in these components, leading to improved range, reduced costs, and increased adoption of electric vehicles.
The growth of the EV market is driven by government regulations, declining battery costs, and increasing consumer awareness of the benefits of electric vehicles. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly transportation system, understanding the major components of electric vehicles is essential for developing more efficient, reliable, and affordable EVs.
Future Outlook
The future of electric vehicles looks promising, with many manufacturers investing heavily in EV technology. The development of new battery chemistries, such as solid-state batteries, is expected to further improve the range and efficiency of EVs. Additionally, advancements in power electronics and charging systems will enable faster and more convenient charging.
As the EV market continues to grow, we can expect to see increased competition and innovation, driving down costs and improving performance. Governments and companies are also investing in the development of EV infrastructure, including charging stations and grid upgrades, to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
In conclusion, the major components of electric vehicles are the building blocks of a sustainable and environmentally-friendly transportation system. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see significant improvements in the performance, efficiency, and affordability of EVs, driving their adoption and transforming the automotive industry forever.