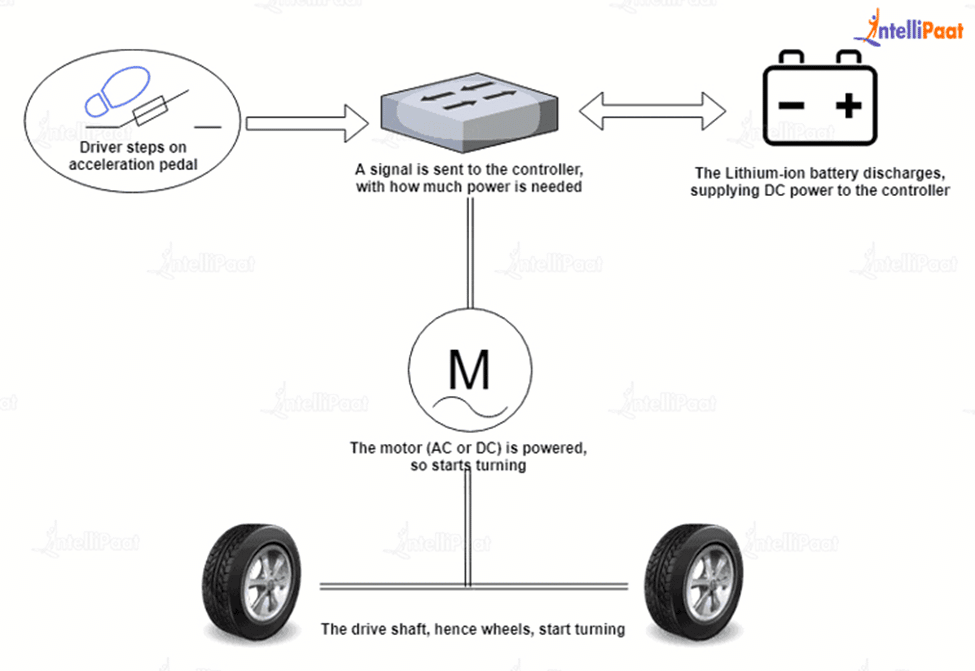
With governments and manufacturers investing heavily in EV technology, the industry is experiencing rapid growth and innovation. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, it's essential to understand the basic components that make up an electric vehicle. In this article, we'll delve into the fundamental components of an EV, exploring their functions, benefits, and significance in the overall design and operation of the vehicle.
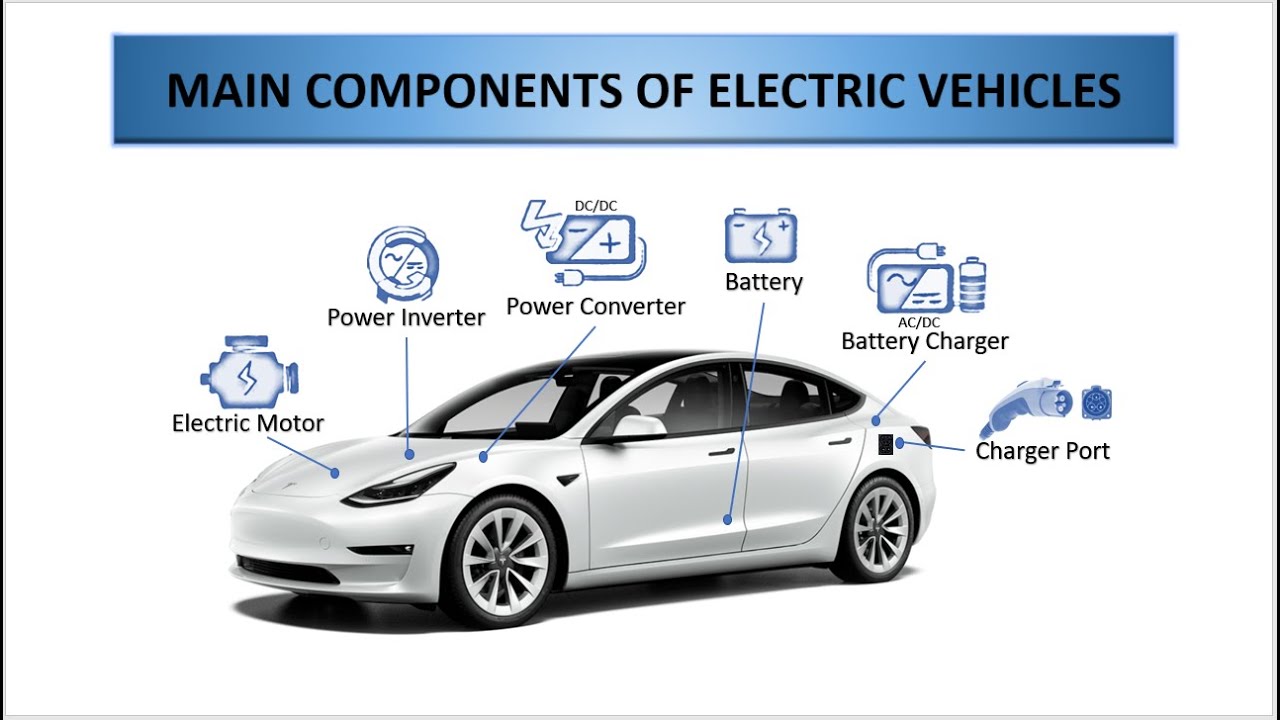
1. Electric Motor
The electric motor is the heart of an electric vehicle, responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. There are several types of electric motors used in EVs, including:
- Permanent Magnet (PM) motors: These motors use a permanent magnet as the rotor, providing high efficiency and reliability.
- Induction motors: These motors use electromagnetic induction to generate torque, offering high performance and durability.
- Switched Reluctance (SR) motors: These motors use a unique design that combines the benefits of PM and induction motors, providing high efficiency and low cost.
Electric motors offer several advantages over traditional internal combustion engines, including:
- High efficiency: Electric motors can achieve efficiency rates of up to 95%, compared to 20-30% for internal combustion engines.
- Low maintenance: Electric motors have fewer moving parts, reducing wear and tear, and minimizing maintenance requirements.
- Instant torque: Electric motors provide instantaneous torque, enabling rapid acceleration and smooth performance.
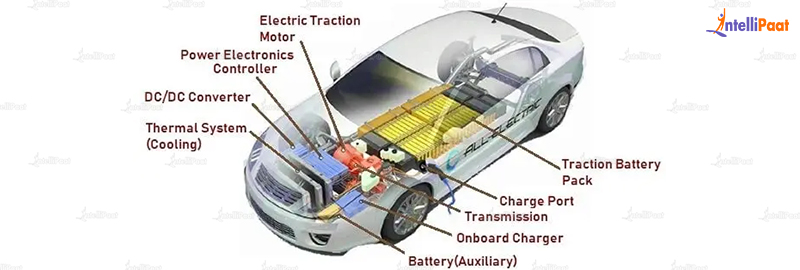
2. Battery Pack
The battery pack is a critical component of an electric vehicle, responsible for storing electrical energy to power the motor. Most EVs use Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) batteries, which offer high energy density, long lifespan, and relatively low cost. The battery pack typically consists of several individual battery cells, connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
The battery pack is designed to:
- Store energy: The battery pack stores electrical energy, which is then used to power the motor.
- Provide power: The battery pack provides power to the motor, enabling the vehicle to move.
- Regulate voltage: The battery pack regulates voltage to ensure stable and consistent power output.
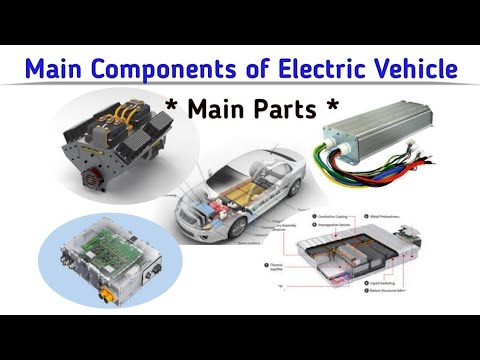
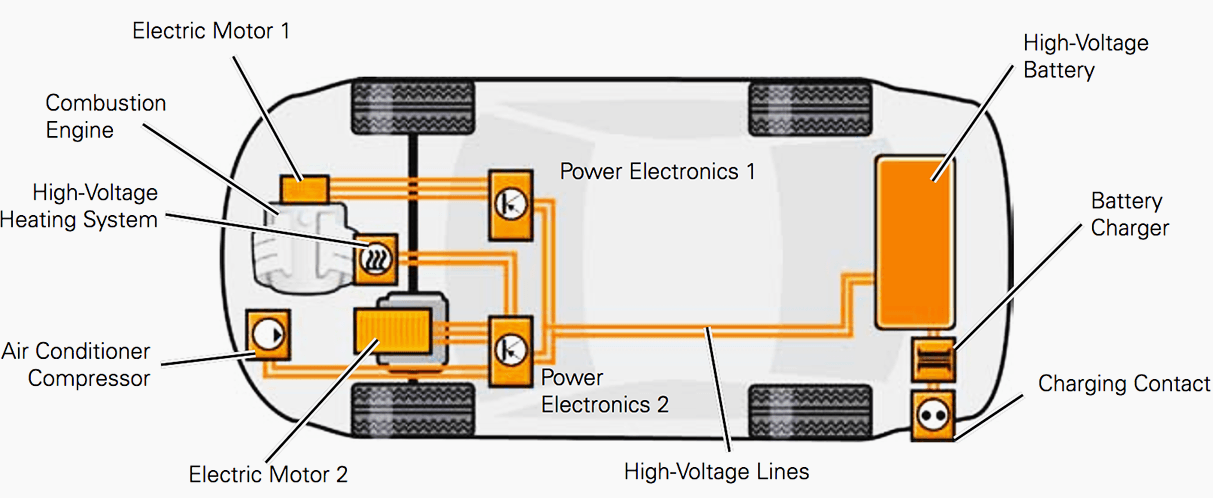
3. Power Electronics
Power electronics play a crucial role in controlling the flow of electrical energy between the battery pack and the motor. The power electronics system consists of several components, including:
- Inverter: The inverter converts DC power from the battery pack to AC power, which is then used to drive the motor.
- Converter: The converter regulates the voltage and current output of the inverter, ensuring stable and efficient power delivery.
- Control unit: The control unit monitors and controls the power electronics system, optimizing performance, efficiency, and safety.
Power electronics enable:
- Efficient power delivery: Power electronics optimize power delivery, minimizing energy losses and maximizing efficiency.
- Regulated voltage: Power electronics regulate voltage output, ensuring stable and consistent power supply to the motor.
- Protection: Power electronics provide protection against overvoltage, overcurrent, and other electrical faults.
4. Transmission and Gearbox
While electric vehicles don't require a traditional transmission system, some EVs use a single-speed or multi-speed gearbox to optimize performance and efficiency. The gearbox is designed to:
- Optimize gear ratio: The gearbox optimizes the gear ratio to achieve the best possible performance, efficiency, and range.
- Reduce energy losses: The gearbox reduces energy losses, minimizing heat generation and maximizing overall efficiency.
5. Charging System
The charging system is responsible for replenishing the battery pack, enabling the vehicle to recharge and prepare for the next journey. Most EVs use a Level 2 (240V) charger, which provides faster charging times and higher power output. The charging system typically includes:
- Onboard charger: The onboard charger converts AC power from the grid to DC power, which is then used to charge the battery pack.
- Charging port: The charging port provides a safe and convenient connection point for the charging cable.
The charging system enables:
- Convenient charging: The charging system provides a convenient and user-friendly charging experience, with options for Level 1 (120V), Level 2 (240V), and DC Fast Charging.
- Faster charging: The charging system offers faster charging times, minimizing downtime and maximizing vehicle availability.
6. Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS is a critical component of an electric vehicle, responsible for monitoring and controlling the battery pack's state of charge, voltage, and temperature. The BMS ensures:
- Safe operation: The BMS ensures safe operation, preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and other battery-related faults.
- Optimized performance: The BMS optimizes battery performance, maximizing range, efficiency, and overall vehicle performance.
- Long battery life: The BMS helps to extend battery life, minimizing degradation and ensuring reliable operation over the vehicle's lifespan.
7. Thermal Management System
The thermal management system is designed to regulate the temperature of the battery pack, motor, and other critical components. The system typically includes:
- Cooling system: The cooling system uses air or liquid cooling to regulate the temperature of the battery pack and motor.
- Heating system: The heating system provides warmth to the battery pack and cabin, ensuring comfortable operation in cold temperatures.
The thermal management system enables:
- Optimized performance: The thermal management system optimizes performance, ensuring that the battery pack and motor operate within their optimal temperature ranges.
- Extended lifespan: The thermal management system helps to extend the lifespan of the battery pack and other critical components, minimizing degradation and ensuring reliable operation.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles are complex systems, comprising numerous components that work together to provide a safe, efficient, and enjoyable driving experience. Understanding the basic components of an EV, including the electric motor, battery pack, power electronics, transmission and gearbox, charging system, battery management system, and thermal management system, is essential for appreciating the technology and innovation that goes into these vehicles. As the EV industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements in these components, leading to improved performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Whether you're a seasoned EV enthusiast or just starting to explore the world of electric vehicles, a deeper understanding of these components will help you appreciate the incredible technology that's driving the future of transportation.