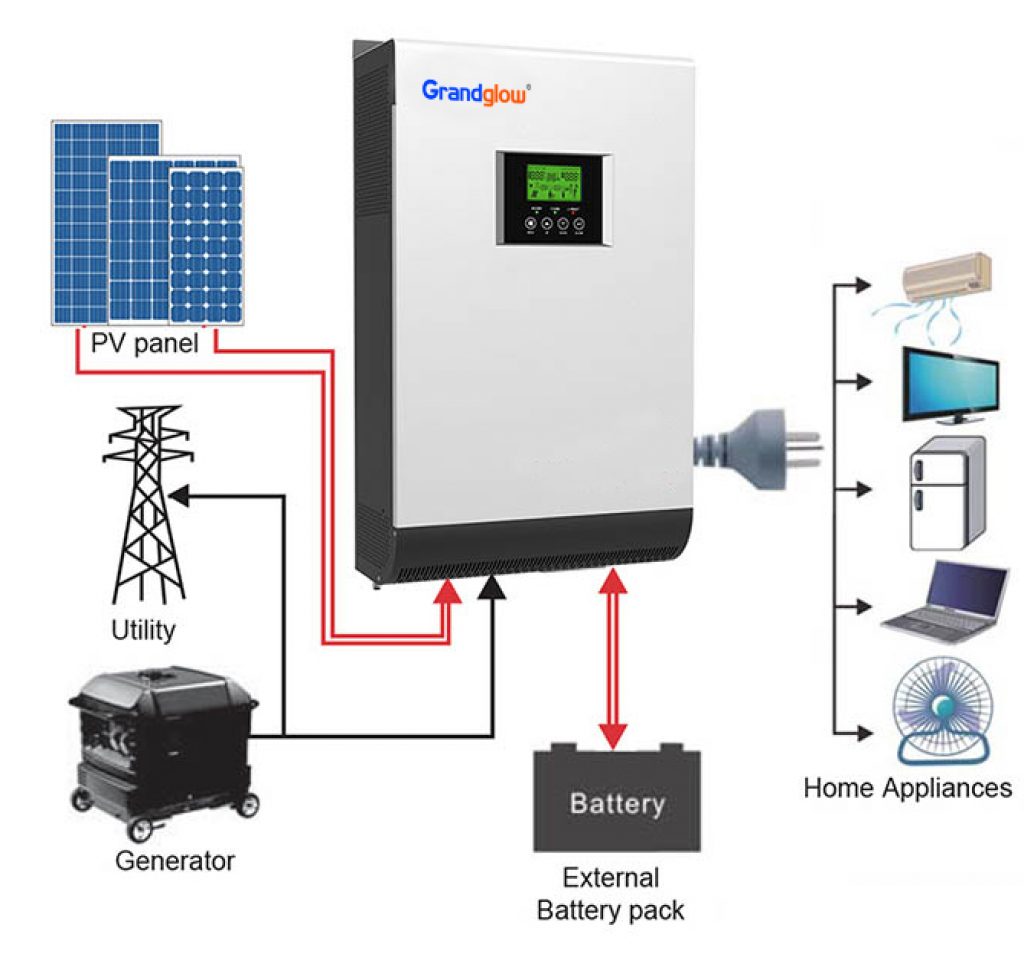
“Solar panel and battery wiring for off-grid homes”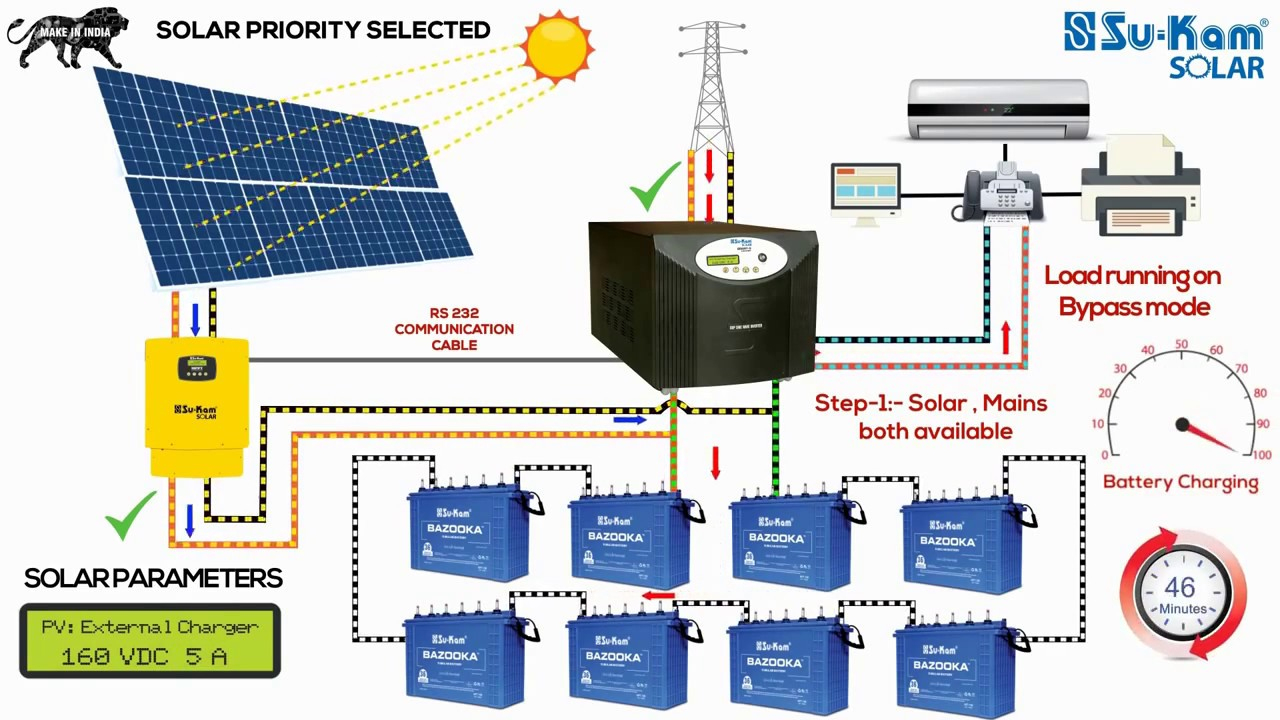
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of wiring, it’s essential to understand the basic components of an off-grid solar system. A typical system consists of:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) modules that convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Charge Controller: This device regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery bank, preventing overcharging and ensuring the batteries are charged efficiently.
- Battery Bank: A collection of deep-cycle batteries that store excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use.
- Inverter/Charger: This device converts the DC power from the battery bank into AC power, suitable for household appliances, and also charges the batteries when the grid is available.
- Wiring and Connectors: The electrical connections between the various components, including the solar panels, charge controller, battery bank, and inverter/charger.
Solar Panel Wiring

When it comes to wiring solar panels, there are several factors to consider. The primary goal is to maximize energy production while minimizing energy losses due to resistance, voltage drop, and other factors. Here are some best practices for solar panel wiring:
- Series and Parallel Connections: Solar panels can be connected in series (positive to negative) to increase the system voltage, or in parallel (positive to positive, negative to negative) to increase the system current. A combination of both series and parallel connections is often used to achieve the desired voltage and current.
- Wiring Size and Type: The wiring size and type should be chosen based on the system’s current and voltage requirements. Thicker wires (lower gauge) are recommended for longer distances or higher current applications.
- MC4 Connectors: MC4 connectors are the standard connector type for solar panels. They are easy to install, waterproof, and suitable for outdoor use.
- Stringing and Branching: When connecting multiple solar panels, it’s essential to use stringing and branching techniques to minimize voltage drop and ensure equal current distribution.

Battery Bank Wiring
The battery bank is a critical component of an off-grid solar system, and proper wiring is essential for safe and efficient operation. Here are some best practices for battery bank wiring:
- Battery Type and Configuration: The type and configuration of the battery bank will determine the wiring requirements. For example, a 12V battery bank may consist of six 2V batteries connected in series.
- Wiring Size and Type: The wiring size and type should be chosen based on the system’s current and voltage requirements. Thicker wires (lower gauge) are recommended for longer distances or higher current applications.
- Battery Interconnects: Battery interconnects are used to connect the batteries in the battery bank. These interconnects should be sized correctly to minimize voltage drop and ensure equal current distribution.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential for safety and to prevent electrical shock. The battery bank should be grounded to the system’s grounding point, and all metal components should be bonded together.

Inverter/Charger Wiring
The inverter/charger is a critical component of an off-grid solar system, as it converts the DC power from the battery bank into AC power for household appliances. Here are some best practices for inverter/charger wiring:
- Wiring Size and Type: The wiring size and type should be chosen based on the system’s current and voltage requirements. Thicker wires (lower gauge) are recommended for longer distances or higher current applications.
- Input and Output Connections: The inverter/charger should have separate input and output connections for the battery bank and AC loads, respectively.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential for safety and to prevent electrical shock. The inverter/charger should be grounded to the system’s grounding point, and all metal components should be bonded together.
- AC Connections: The AC connections should be made to the household electrical panel, using a suitable AC connector type (e.g., 240V, 30A).
System Monitoring and Control
A well-designed off-grid solar system should include monitoring and control components to ensure safe and efficient operation. Here are some best practices for system monitoring and control:
- System Monitoring: A system monitor should be installed to track the system’s performance, including solar panel output, battery state of charge, and AC load demand.
- Charge Controller Settings: The charge controller settings should be adjusted to optimize the charging process, taking into account the battery type, temperature, and other factors.
- Inverter/Charger Settings: The inverter/charger settings should be adjusted to optimize the AC output, taking into account the household load profile and other factors.
- Alarm and Notification Systems: An alarm and notification system should be installed to alert the homeowner of any system issues or faults.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a top priority when it comes to solar panel and battery wiring for off-grid homes. Here are some essential safety considerations:
- Electrical Shock: Electrical shock can occur when working with electrical systems, especially when there are live wires or charged batteries. Proper grounding, bonding, and insulation are essential to prevent electrical shock.
- Fire Risk: Fire risk is associated with electrical systems, especially when there are faulty or damaged components. Regular maintenance, inspection, and testing are essential to minimize the risk of fire.
- Overcharge Protection: Overcharge protection is crucial to prevent damage to the batteries and other system components. A properly configured charge controller and inverter/charger can help prevent overcharge conditions.
- Lightning Protection: Lightning protection is essential for off-grid solar systems, as lightning strikes can damage the system components and pose a safety risk. A suitable lightning protection system should be installed to protect the system.
Conclusion
Solar panel and battery wiring for off-grid homes requires careful planning, design, and installation to ensure a safe, efficient, and reliable energy system. By following the best practices outlined in this article, homeowners and installers can create a well-designed system that meets the needs of the household while minimizing the risk of electrical shock, fire, and other hazards. Remember to always consult local electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards when designing and installing an off-grid solar system. With proper planning and execution, off-grid solar systems can provide a sustainable, renewable, and reliable source of energy for homes and communities around the world.