“Residential solar power wiring schematics”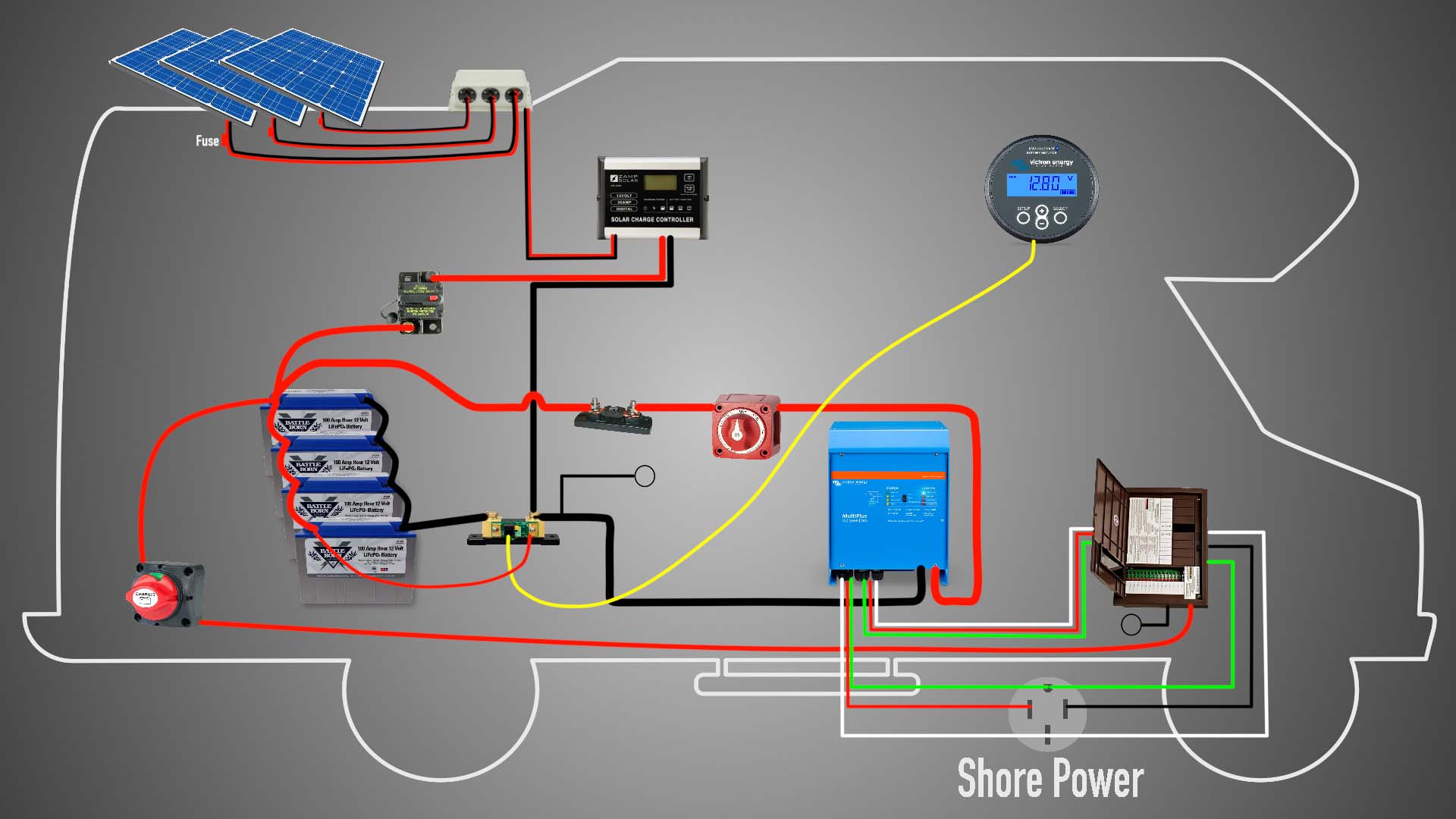
Understanding the Basics of Residential Solar Power Systems
Before we dive into the wiring schematics, it’s essential to understand the basic components of a residential solar power system. These include:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Mounting System: This is the framework that supports the solar panels and ensures they are secure and angled for optimal energy production.
- Inverter: This device converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is usable in the home.
- Charge Controller: This component regulates the flow of energy between the solar panels, battery bank (if present), and the inverter.
- Battery Bank: This is an optional component that stores excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use.
- Electrical Panel: This is the main distribution panel that connects the solar power system to the home’s electrical grid.

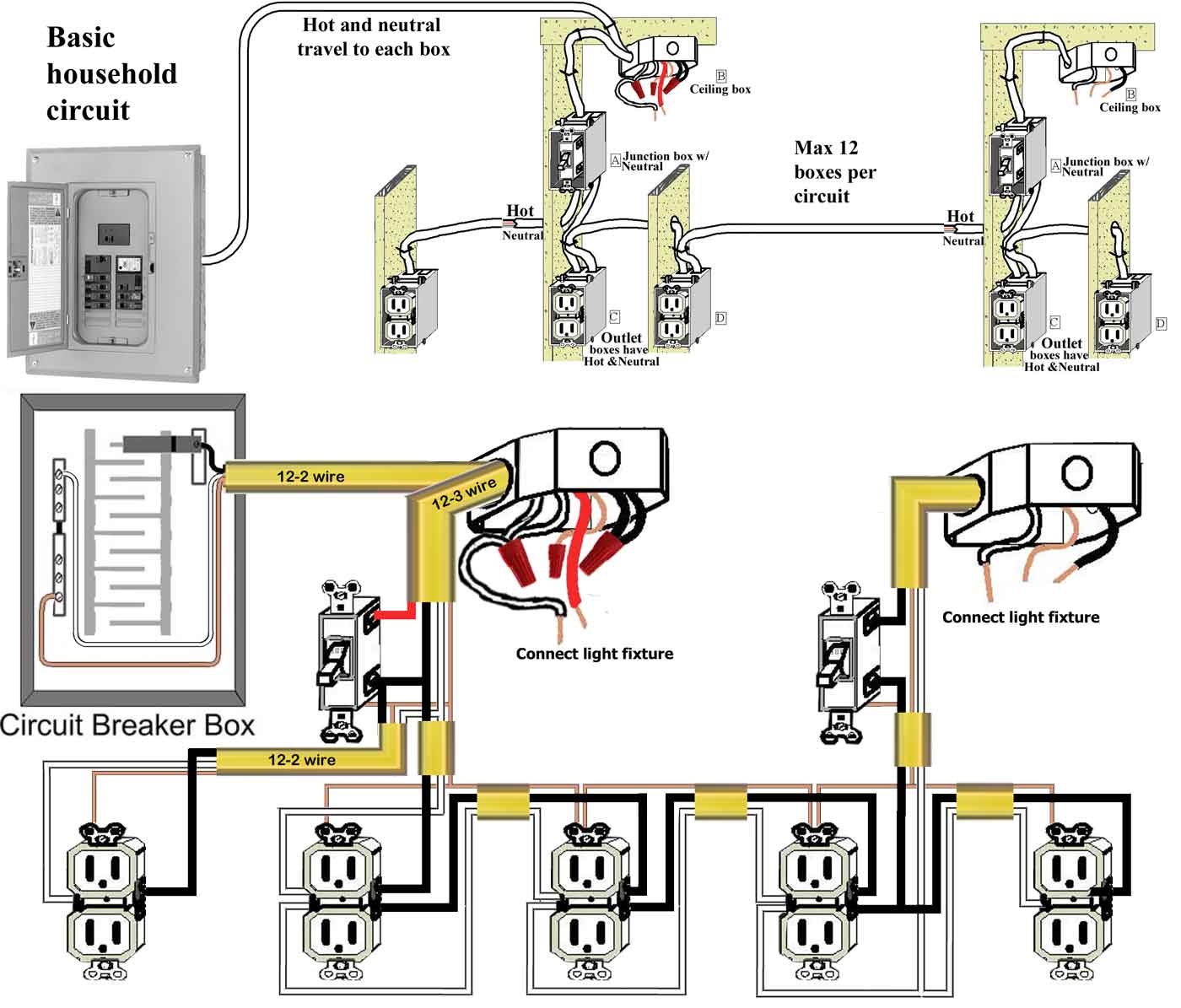
Wiring Schematics: An Overview
Residential solar power wiring schematics are diagrams that illustrate the electrical connections between the various components of the solar power system. These schematics are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient energy transfer, as well as for troubleshooting and maintenance. A typical wiring schematic for a residential solar power system includes:
- Solar Panel Wiring: This shows the connections between the solar panels, including the positive and negative terminals, and the wiring to the inverter or charge controller.
- Inverter Wiring: This illustrates the connections between the inverter, electrical panel, and the utility grid (if grid-tied).
- Charge Controller Wiring: This shows the connections between the charge controller, solar panels, battery bank (if present), and the inverter.
- Battery Bank Wiring: This illustrates the connections between the battery bank, charge controller, and inverter (if present).
- Grounding System: This shows the connections between the solar panels, mounting system, and the grounding system, which ensures electrical safety.

Types of Residential Solar Power Wiring Schematics
There are several types of residential solar power wiring schematics, each with its own unique characteristics and applications:
- Grid-Tie System: This is the most common type of residential solar power system, where the solar panels are connected to the utility grid through an inverter.
- Off-Grid System: This type of system is not connected to the utility grid and relies on a battery bank to store excess energy.
- Hybrid System: This system combines a grid-tie system with a battery bank, providing a backup power source during grid outages.
- Microinverter System: This system uses multiple microinverters, each connected to a single solar panel, to optimize energy production and reduce voltage drop.
Designing Residential Solar Power Wiring Schematics
Designing a residential solar power wiring schematic requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- System Size: The size of the solar power system, including the number of solar panels, inverter, and battery bank (if present).
- Electrical Load: The electrical load of the home, including the total wattage of appliances and lighting.
- Voltage and Current: The voltage and current requirements of the solar power system, including the inverter, charge controller, and battery bank (if present).
- Grounding and Bonding: The grounding and bonding requirements for the solar power system, including the solar panels, mounting system, and electrical panel.
Best Practices for Residential Solar Power Wiring Schematics
To ensure safe and efficient energy transfer, it’s essential to follow best practices when designing and installing residential solar power wiring schematics:
- Use UL-Listed Components: Only use components that are listed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) for safety and reliability.
- Follow NEC Guidelines: Follow the guidelines set forth by the National Electric Code (NEC) for electrical installations.
- Use Proper Wiring and Connectors: Use proper wiring and connectors to ensure secure and reliable connections.
- Label and Document: Label and document the wiring schematic and electrical connections for future reference and maintenance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When designing and installing residential solar power wiring schematics, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to safety hazards, reduced efficiency, and system failure:
- Inadequate Grounding: Inadequate grounding can lead to electrical shock and system failure.
- Insufficient Wire Sizing: Insufficient wire sizing can lead to voltage drop and reduced system efficiency.
- Incorrect Component Selection: Incorrect component selection can lead to system failure and reduced efficiency.
- Poor Workmanship: Poor workmanship can lead to safety hazards and system failure.
Conclusion
Residential solar power wiring schematics are a critical component of a safe and efficient solar power system. By understanding the basics of residential solar power systems, designing and installing wiring schematics, and following best practices, homeowners, electricians, and solar installers can ensure a reliable and efficient energy transfer from the solar panels to the home’s electrical system. Remember to avoid common mistakes and follow NEC guidelines and UL listings to ensure a safe and efficient solar power system. With the right wiring schematic, you can enjoy the benefits of renewable energy and reduce your reliance on the grid.
Additional Resources
For further information on residential solar power wiring schematics, please refer to the following resources:
- National Electric Code (NEC)
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
- International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI)
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA)
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can ensure a safe and efficient residential solar power system that meets your energy needs and contributes to a cleaner environment.