“Standalone solar power wiring layout”
Introduction to Standalone Solar Power Systems
A standalone solar power system consists of several key components, including:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) modules that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Charge Controller: This device regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and ensuring safe operation.
- Batteries: These are the energy storage devices that store excess energy generated by the solar panels during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
- Inverter: This device converts the DC electricity stored in the batteries to alternating current (AC) electricity, which is usable by household appliances.
- Wiring and Electrical Panels: These are the components that connect the various system components together, allowing for safe and efficient energy transfer.
Design Considerations for Standalone Solar Power Wiring Layout

When designing a standalone solar power wiring layout, there are several key considerations to keep in mind:
- System Size and Configuration: The size and configuration of the system will depend on the energy requirements of the building or application. A larger system will require more solar panels, batteries, and a more complex wiring layout.
- Energy Storage: The type and size of batteries used will impact the wiring layout, as will the charging and discharging requirements of the system.
- Inverter Selection: The type and size of inverter used will depend on the system configuration and energy requirements.
- Wiring and Electrical Panel Selection: The type and size of wiring and electrical panels used will depend on the system configuration and energy requirements.
- Safety and Code Compliance: The wiring layout must comply with local electrical codes and safety standards to ensure safe operation and prevent electrical shock or fire hazards.

Key Components of a Standalone Solar Power Wiring Layout
The following are the key components of a standalone solar power wiring layout:
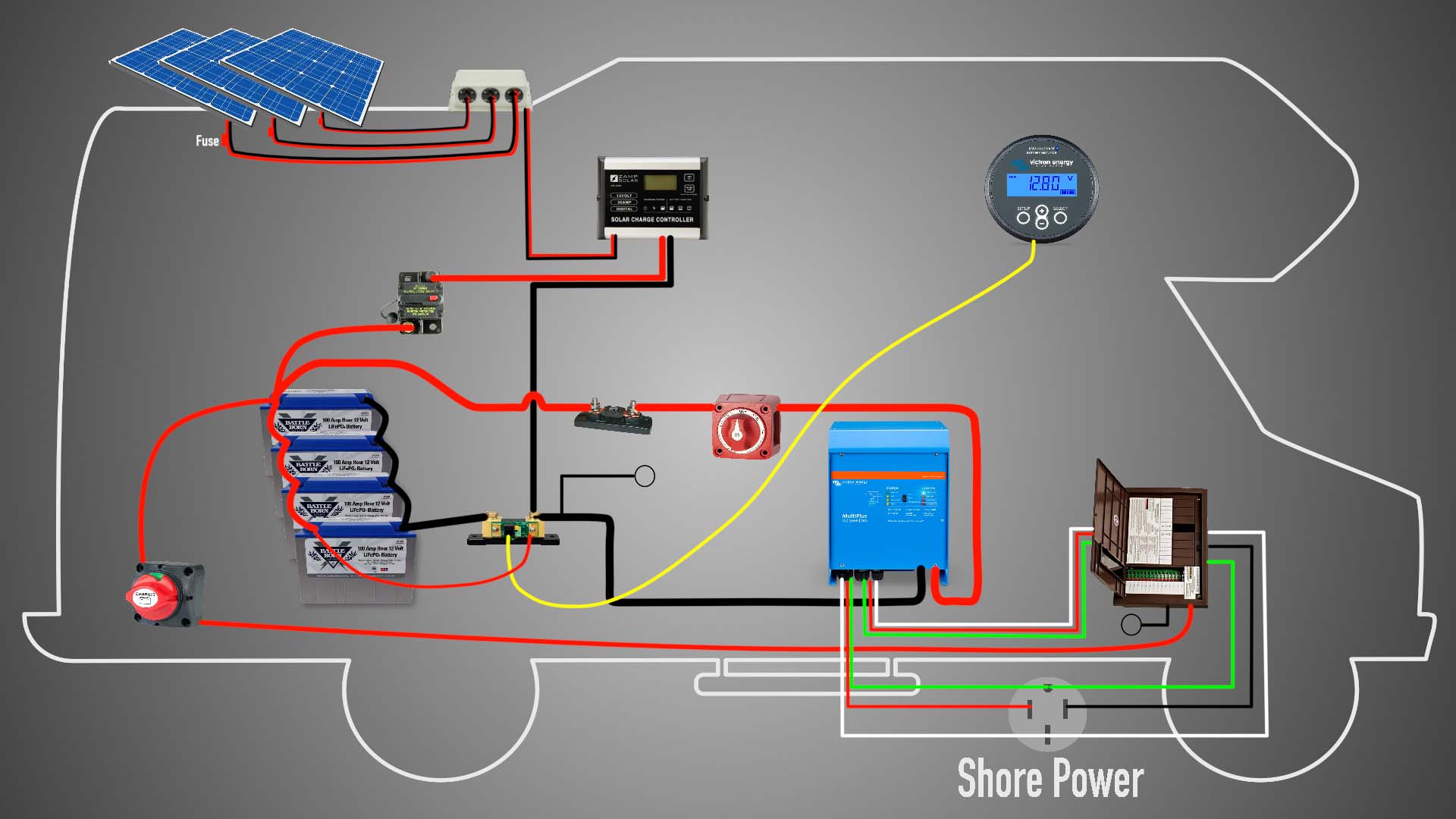
- Solar Panel Array Wiring: This involves connecting the solar panels together in series and/or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current output.
- Charge Controller Wiring: This involves connecting the charge controller to the solar panel array and batteries, ensuring safe and efficient energy transfer.
- Battery Bank Wiring: This involves connecting the batteries together in series and/or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
- Inverter Wiring: This involves connecting the inverter to the battery bank and electrical panel, ensuring safe and efficient energy transfer.
- Electrical Panel Wiring: This involves connecting the electrical panel to the inverter, batteries, and other system components, ensuring safe and efficient energy transfer.
Best Practices for Standalone Solar Power Wiring Layout
To ensure a safe and efficient standalone solar power wiring layout, follow these best practices:
- Use Properly Sized Wiring: Use wiring that is properly sized for the system, taking into account the voltage, current, and power requirements.
- Use Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Use fuses and circuit breakers to protect the system from overcurrent and short-circuit faults.
- Use Grounding and Bonding: Use grounding and bonding to ensure safe operation and prevent electrical shock or fire hazards.
- Label and Document the System: Label and document the system, including the wiring layout, system components, and electrical connections.
- Test and Inspect the System: Test and inspect the system regularly to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Standalone Solar Power Wiring Layout
To avoid common mistakes in standalone solar power wiring layout, follow these guidelines:
- Avoid Overloading the System: Avoid overloading the system by ensuring that the wiring and electrical panels are properly sized for the energy requirements.
- Avoid Improper Grounding and Bonding: Avoid improper grounding and bonding by ensuring that the system is properly grounded and bonded to prevent electrical shock or fire hazards.
- Avoid Inadequate Ventilation: Avoid inadequate ventilation by ensuring that the system is installed in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating and reduce the risk of electrical shock or fire hazards.
- Avoid Poor Quality Components: Avoid poor quality components by selecting system components from reputable manufacturers and following proper installation procedures.
- Avoid Lack of Maintenance: Avoid lack of maintenance by regularly inspecting and testing the system to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a standalone solar power wiring layout requires careful planning and attention to detail to ensure safe and efficient operation. By following the key considerations, best practices, and avoiding common mistakes outlined in this article, you can design and install a reliable and efficient standalone solar power system that meets your energy needs and reduces your carbon footprint. Remember to always follow local electrical codes and safety standards, and consult with a qualified solar professional if you are unsure about any aspect of the installation process.
Additional Resources
For more information on standalone solar power wiring layout, refer to the following resources:
- National Electric Code (NEC): The NEC provides guidelines for electrical wiring and safety standards.
- International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI): The IAEI provides resources and training for electrical inspectors and professionals.
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): The SEIA provides resources and guidance on solar energy systems and installation best practices.
- Local Electrical Codes and Regulations: Check with your local authorities for specific electrical codes and regulations in your area.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can ensure a safe and efficient standalone solar power wiring layout that meets your energy needs and contributes to a sustainable future.





